
The ion-absorbed type minerals in southern china are critical rare earth resources, which are rich in heavy rare earth elements (REEs). Constituents of heavy REEs in the minerals arrive at 30-80%.
To develop sustainable and effective separation technologies for ion-absorbed type minerals, Prof. SUN Xiaoqi and his research group from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM), Chinese Academy of Sciences have made new progresses on the fields of extraction mechanism, system and material. The works has been recently published inInd. Eng. Chem. Res., AIChE J.and ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng..
Investigations of the complexation of REEs with phenoxyacetic acid-related ligand help in the development of efficient extractants for REEs separation. The structures were characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, FT-IR, and elemental analysis. The hydrogen binding energies of ligands were studied by density functional theory (DFT). Atoms in molecules (AIMs) analysis revealed the presence of dominant non-covalent interactions between REE and O atoms and an ionic character for the complexation interaction.
Also, synergistic extraction between quaternary phosphonium type ionic liquids in the field of solvent extraction was reported. The formed reversed micelles contributed to increase extractability of the synergistic system for REEs to a considerable extent. On one hand, million tons of saponification wastewaters from acidic extractants may be avoided by developing the bifunctional ionic liquid extractants. On the other hand, the novel synergistic extraction offers an effective strategy to increase the extractabilities of industrial extractants.
Multi-stage extraction using functional ionic liquid as extractant for different REEs separation was developed. After five stages of extraction sections and four stages of scrubbing sections, the Lu(III) was successfully separated from Y(III) using the fractional extraction process. Moreover, stripping by distilled water was achieved in ionic liquid based extraction for REE, which contributed to decrease the consumption of acid to a considerable extent.
Moreover, synergistic effect produced by ionic liquid extractants in the field of adsorption was reported. The data from this work show that distribution coefficient and synergistic enhancement coefficient of Lu(III) extracted by the ionic liquid extractants in impregnated resin are pronounced higher than those in solvent extraction. The elimination of third phase from ionic liquid extractants is a remarkable advantage of adsorption over solvent extraction.
This works was supported by ‘Hundred Talent Program’ from Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China and Science and Technology Major Projects of Fujian Province.
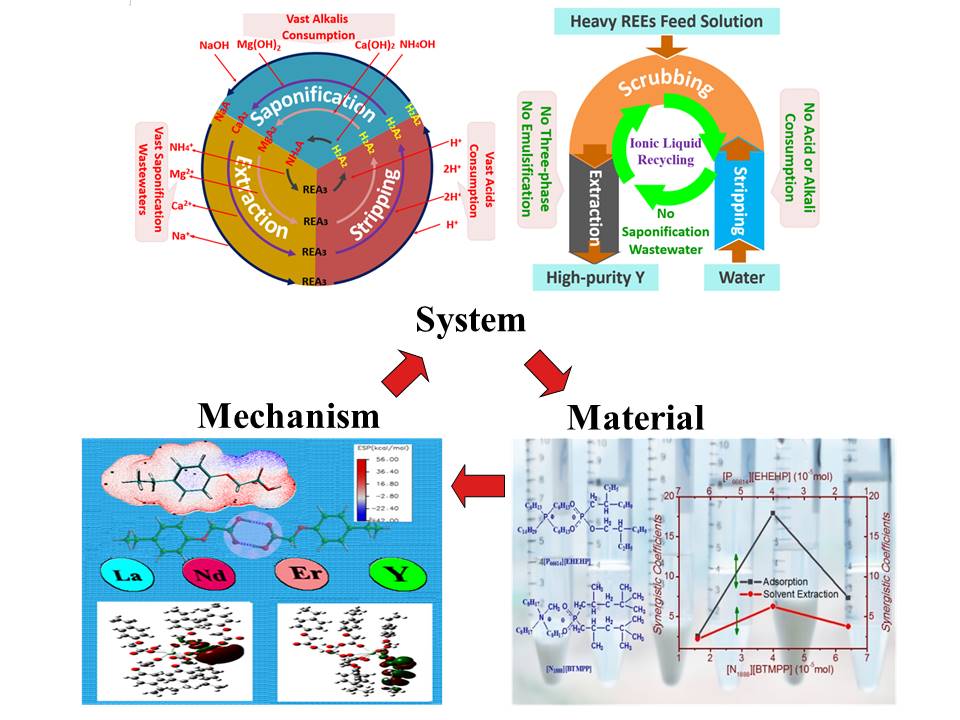
Representation of separation system, mechanism and material studies for rare earth (Image by Prof. SUN's group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

