
Rapid Separation and Detection Group in Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) realized two-dimensional separation detection of triacetone triperoxide (TATP) and hexamethylene trioxide diamine (HMTD) in complex matrices recently. It bases on the dopant-assisted positive photoionization ion mobility spectrometry, with time-resolved thermal desorption introduction. The analysis time was less than 10s, and the limits of detection (LODs) achieved to nanogram (ng) levels. This result has been published on Analytical Chemistry (DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04830).
Researchers Realize Two-dimensional Separation Detection of TATP and HMTD in Complex Matrices (Image by JIANG Dandan and PENG Liying)
Due to the simple synthesis procedures with the easy-to-obtain materials, TATP and HMTD have been used in the terrorist attacks, such as the multiple Belgium bombings on March 22, 2016, the Paris attacks in 2015 and the London Subway attacks in 2005.
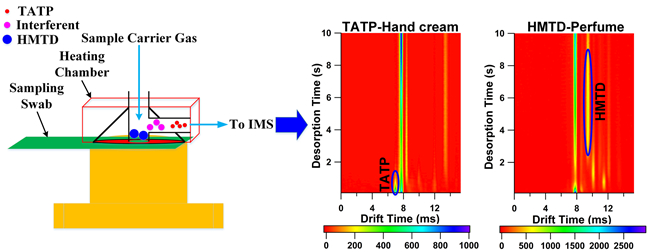
Negative ion mode ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) has been successfully used for the detection of nitro-based explosives, such as 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) and pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN). However, since TATP and HMTD contain no nitro groups, it is difficult to be detected by negative IMS. Furthermore, TATP and HMTD are often concealed in complex matrices, and the interfering agents would influence their detection.
Professor LI Haiyang’s group developed a dopant-assisted positive photoionization ion mobility spectrometry coupled with time-resolved thermal desorption introduction. With the different volatility between TATP/HMTD and the interfering agents, they realized the two-dimensional separation detection of TATP and HMTD in complex matrices. The analysis time was less than 10s and the LODs reached 23.3 and 0.2 ng, respectively.
This new technique broadens the detectable explosive species for IMS. It can reduce the undetected probability during explosive screening and offer the great potential for security services in public places, such as airport and subway station.
Rytrum Technology (Dalian) Co., Ltd. and Rapid Separation and Detection Group have signed an agreement for patents transfer. They plan to apply the new technique into the mass-produced IMS explosives detectors.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

