
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) and Shenzhen University established a basic N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) liquid exfoliation method to produce phosphorene with excellent water stability, controllable size and layer number, as well as high yield. It’s a basic solvent exfoliation, evolution of Raman scattering, and applications to ultra-fast photonics.
Black phosphorus (BP) has large potential in electronics and optoelectronics due to the thickness-dependent bandgap structure, high carrier mobility, and anisotropic photoelectronic properties. The wide-range adjustability and direct bandgap of BP are expected to emulate graphene in optoelectronics. However, to some extend, the absence of effective methods for large-scale production of few-layered BP hindered the application of BP.
Phosphorene of one to four layers exhibits layer-dependent Raman scattering characteristics. Based on this phenomenon, a fast and efficient means for in situ determination of the thickness (layer number) of phosphorene has been built. The linear and nonlinear ultrafast absorption behavior of the as-exfoliated phosphorene is investigated systematically by UV-visible-NIR absorption and Z-scan measurements. By taking advantage of the unique nonlinear absorption, the applicability of ultrashort pulse generation to optical saturable absorbers is demonstrated.
In addition to the unique fabrication technique, this work reveals the large potential of phosphorene in ultrafast photonics. The paper entitled From black phosphorus to phosphorene: basic solvent exfoliation, evolution of Raman scattering, and applications to ultra-fast photonics, has been published in Adv. Funct. Mater.
The research group includes Professor YU Xuefeng from SIAT and Professor ZHANG Han from Shenzhen University. This work was supported by the Shenzhen Overseas High Level Talents Peacock Team Project, NSFC and the Science and Technology Key Project of Shenzhen.
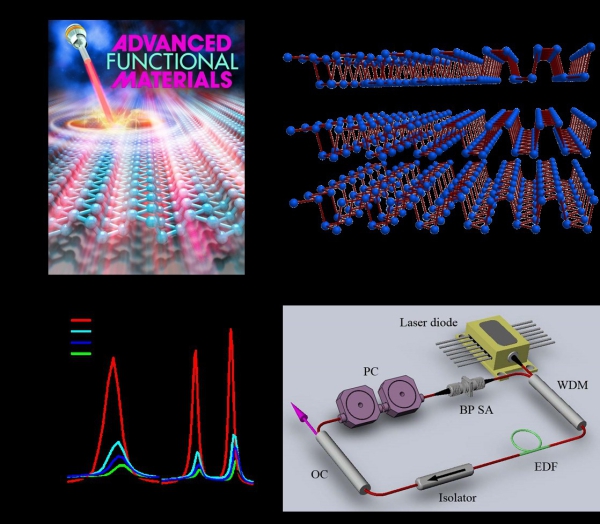
Figure caption: Back cover image of Adv. Funct. Mater. (a); 2D view of the layered BP structure (b); Raman spectra of bulk BP and phosphorene with different numbers of layers (c); Schematic of the passively mode-locked fiber laser based on the phosphorene saturabler absorber (d).

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

