
The radiation process and algorithm in atmosphere-ocean system is crucial to understand the reason of climate change and development of marine resources. Co-supervised by scientists from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. Teruyuki Nakajima of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, PhD candidate SHI Chong studied the radiative transfer and remote sensing in atmosphere-ocean system, and developed an analytical approximation method to calculate the radiation flux in atmosphere-ocean system using Eddington approximation based on the proposed formula of ocean reflection.
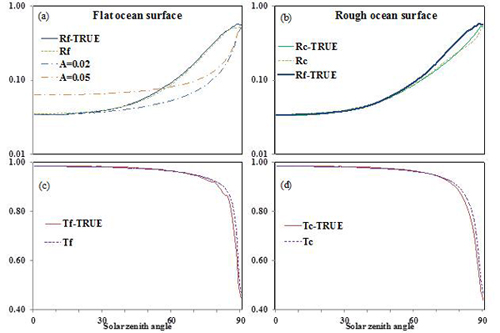
Reflectivity at the top of the atmosphere and transmissivity just above the sea surface. Solid lines (symbolized by “R/T-TRUE”) show exact values calculated by a radiative transfer model. Chained lines (symbolized by “A”) show values for a Lambertian underlying surface. Dashed lines (symbolized by “R/T”) show the values calculated by the method in this paper. (a/c) Flat ocean surface (symbolized by Rf/Tf); (b/d) rough ocean surface with 10 m/s wind velocity at 10 m height above the ocean surface (symbolized by Rc/Tc). (Figure plotted by IAP)
It has been proved that the proposed analytical approximation method is useful in the radiation scheme of GCM, while it is not sufficient in the satellite remote sensing. Therefore the team improved a vector radiative transfer model by coupling marine biology-optic module as well as radiative transfer module. They take into account the influence of seawater, salinity, temperature, chlorophyll, inorganic suspended particles and yellow substance, and studied the effects of oceanic particles, aerosol and wind speed on radiation process based on the improved model. "We compared the improved model with the standard water radiative transfer problems defined by Mobley et al, and we are pleased to find the performance of improved model in processing water radiation process is good." Said SHI.
Based on the improved model which accurately simulating the radiation process in the atmosphere-ocean system, the team developed an algorithm of simultaneous retrieval of aerosol, wind speed and chlorophyll using non-linear optimal estimation theory.
The studies have recently been published in Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer and Advances in Atmospheric Sciences.
References:
Mobley, C. D., and Coauthors, 1993: Comparison of numerical models for computing underwater light fields. Applied Optics, 32, 7484-7504.
C. Shi, and T. Nakajima*, 2015: The Eddington approximation calculation of radiation flux in the atmosphere–ocean system. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 157, 34-41.
C. Shi, P. C. Wang*, T. Nakajima, Y. Ota, S. C. Tan, G. Y. Shi. 2015: Effects of ocean particles on the upwelling radiance and polarized radiance in the atmosphere-ocean system. Adv. Atmos. Sci., doi: 10.1007/s00376-015-4222-8.
Contact:
Dr. SHI Chong
Key Laboratory of Middle Atmosphere and Global Environmental Observation (LAGEO), Institute of Atmospheric Physics
E-mail: shic@mail.iap.ac.cn

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

