
Streptothricins are atypical aminoglycoside antibiotics possessing antibacterial and antifungal activities. Zhongshengmycin, a product of streptothricins, is widely used as agriculture antibiotic for crop protection. A defect of this product is that it contains various streptothricin components which make product quality control very difficult.
CHEN Yihua’s lab at State Key Laboratory of Microbial Resources, Institute of Microbiology of Chinese Academy of Sciences has devoted to understanding the biosynthetic mechanism of streptothricins, manipulating their biosynthetic pathway and improving the related product qualities. In this study, they elucidated the biosynthetic pathway of the D-gulosamine moiety and found that two novel enzymatic catalysts were involved in this process. The study has been published on Angew. Chem. Int. Ed..
The biosynthesis of the rare sugar moiety D-gulosamine is depicted as the following figure. At first, a glycosyltransferase StnG adds a D-GalNAc from UDP-D-GalNAc to the guanidino-imine of streptolidine. Then, StnJ catalyzes the epimerization of the 9-OH and StnQ is a carbamoyltransferase installing a carbamoyl group at 12-OH. Finally, StnI removes the acetyl group from 8-NH to form 12-carbamoyl-streptothrisamine. StnG is an unprecedented GT-A fold guanidino-imine glycosyltransferase and StnI represents a novel type of LmbE acetyltransferase recognizing non-D-GlcNAc substrates.
This work was supported by the grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China and 'the 100 Talents Project' of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
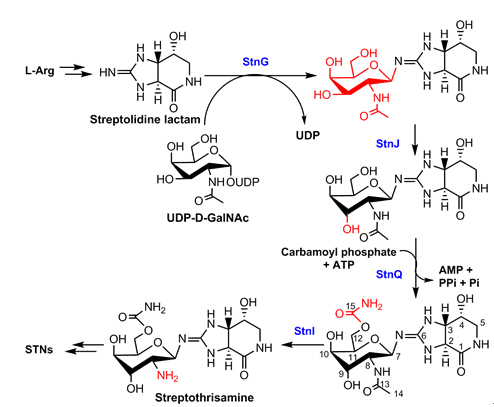
The proposed biosynthetic pathway of D-GulN moiety in streptothricins. (Image by IMCAS)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

