
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a sensor of cellular energy status. Once activated, it switches on catabolic pathways that generate ATP, while switching off biosynthetic pathways. These effects suggest that AMPK activators might be useful for treatment and/or prevention of type 2 diabetes. However, there are not many AMPK small-molecule direct activators discovered so far, partly because the classical screening methods like Filter assay are restricted to their high-cost and low-throughput characters.
HTRF (Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence) method has been used to establish kinase activity assay, which has features like low-cost, high-throughput, easy-operating and good repeatability. Using HTRF assay, Researchers identified and structure optimized a series of AMPK activators: 20(S)-protopanoxadiol (PPD) was originally identified from high throughput screening as a small molecule activator of AMPK through the allosteric activation of heterotrimerα2β1γ1.
Ginseng has been used as drug for over 2,000 years, the main Ingredients of it is ginsenosides, which has many pharmacological activity, including lowering blood pressure, anti-diabetic, anti-oxidation, anti-depressants and anti-cancer. Protopanoxadiol (PPD) was the main plasma metabolites of ginsenosides based on literatures, and it may have potential lipid-lowering and anti-diabetic effects.
The discovery of PPD’s AMPk activating effect provides new mechanism of its pharmacological activity as a natural product structure. In order to enhance its potency at AMPK and structure-activity relationship study, PPD analogues were designed, synthesized, and evaluated in pharmacological AMPK activation assays.
Moreover, the compounds could activate AMPK without affect mitochondrial membrane potential in HepG2 cells, suggesting these compounds do not activated AMPK indirectly through inhibit mitochondrial respiration. And the compounds could also inhibit lipid synthesis in HepG2 cells by activating AMPK.
The paper has been published in European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry(2014 (79):340-349).
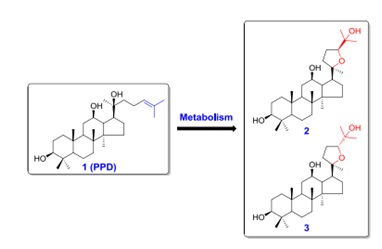
The major metabolites of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol in humans (Image by SIMM)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

