On the basis of a systematic analysis of nearly 40 billion cosmic ray events in a nine-year observation, a Sino-Japanese consortium of Tibet Air Shower Arrays (known as the Tibet ASγCollaboration) reported their work in the Oct. 20 issue of
Science. The feat is hailed as a milestone achievement in the studies of cosmic studies.
The Tibet Air Shower Array experiment (known as the Tibet ASγexperiment) has been conducted by researchers from the CAS Institute of High Energy Physics and foreign colleagues at Yangbajing (4300 m above sea level) in Tibet, China, since1990. The array was expended and upgraded in the following years.
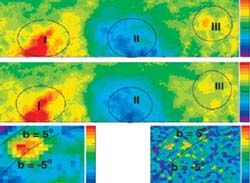
The researchers present two-dimensional high-precision anisotropy measurement for energies from a few to several hundred teraelectronvolts (TeV), using the large data sample of the Tibet Air Shower Arrays. Besides revealing finer details of the known anisotropies, a new component of Galactic cosmic ray anisotropy in sidereal time is uncovered around the Cygnus region direction. For cosmic-ray energies up to a few hundred TeV, all components of anisotropies fade away, showing a corotation of Galactic cosmic rays with the local Galactic magnetic environment. These results have broad implications for a comprehensive understanding of cosmic rays, supernovae, magnetic fields, and heliospheric and Galactic dynamic environments.





