
Newsroom
A research team led by Prof. LIU Yong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Science has developed an innovative method to enhance multi-robot global localization (MR-GL).
Their new approach, named Semantic-Geometric Triple-constraint based Multi-Robot Global Localization (SGT-MGL), demonstrates marked improvements in both accuracy and robustness of robot positioning in dynamic and large-scale environments.
The findings were recently published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters.
MR-GL enables robots to determine their positions relative to one another within a shared map—an essential capability for coordinated robotic systems. While vision-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) has gained popularity for its low cost and rich environmental data, it struggles in scenarios where robots start from unknown locations, encounter drastically different viewpoints, or operate in environments that change rapidly.
To address these limitations, the researchers introduced SGT-MGL, a graph-matching-based global localization framework that fuses semantic and geometric data through a triple-constraint mechanism. This innovative integration significantly boosts the system's resilience and precision.
At the core of the system is the extraction of semantic and geometric features from objects in the environment, which are used to construct a topological graph representing spatial relationships. To enhance object distinctiveness and ensure consistency across various viewpoints, the researchers designed a triangle-based descriptor incorporating semantic labels and relative distances.
To further improve robustnes, they introduced a 3D histogram descriptor that integrates semantic categories, spatial angles, and pairwise distances. This composite descriptor strengthens the system's adaptability in fluctuating environments.
SGT-MGL also employs a coarse-to-fine localization strategy. The process begins by filtering key points using global geometric structures, followed by a multi-level graph matching phase that refines the results through a combination of local and global information. This enables accurate six degrees-of-freedom (6-DoF) pose estimation.
Experimental results validated that SGT-MGL significantly enhances localization performance in complex and dynamic settings. Its triple-constraint framework not only ensures robustness across varying viewpoints but also maintains computational efficiency.
This advancement provides key technical support for multi-robot collaboration in future applications, such as smart hospitals and intelligent factories, according to the team.
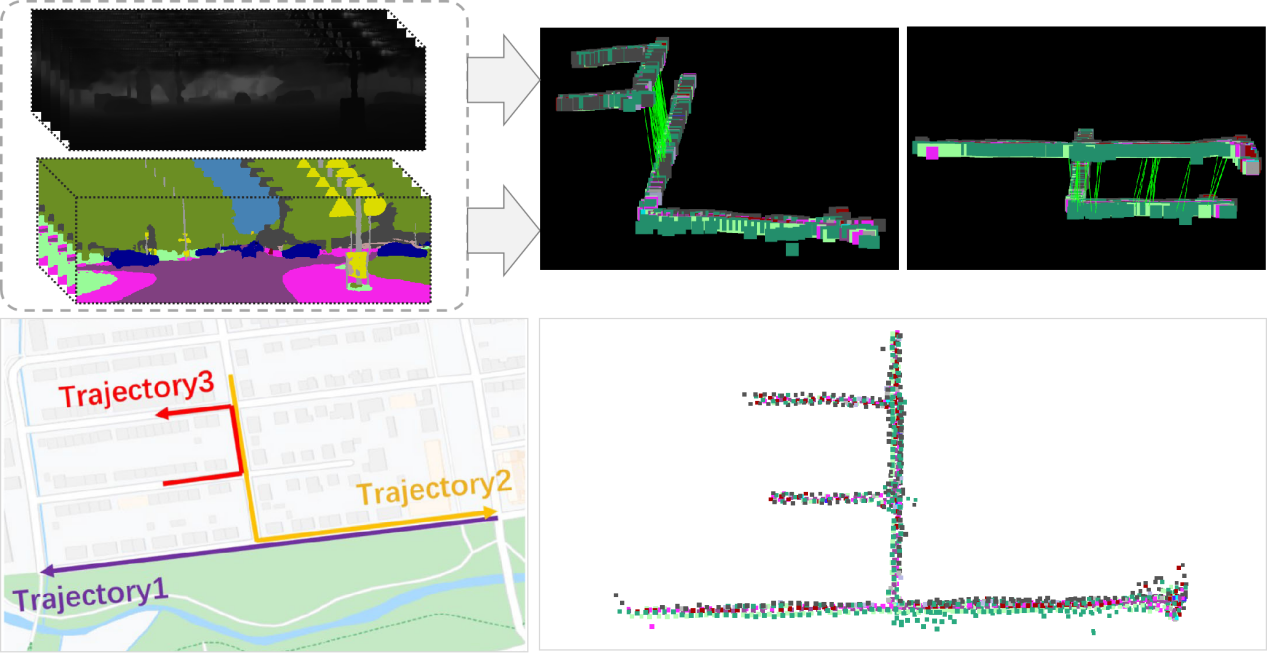
Application of the proposed method for multi-robot global localization on the KITTI08 sequence dataset, using semantic segmentation and depth image as inputs. The bottom right corner shows the composite map generated by merging multiple individual maps. (Image by WANG Fan)
