
Newsroom
Transient Ca2+ fluctuations on the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) can induce liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of the autophagy initiation complex FIP200, forming FIP200 puncta and triggering autophagosome formation. However, the mechanisms by which these transient Ca2+ fluctuations persist during autophagy induction, and how they are decoded to trigger the formation of FIP200 puncta, remain unclear.
On December 31, 2024, a study led by Prof. ZHONG Hong at the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, published in Molecular Cell, sheds light on the role of CaMKIIβ in responding to ER Ca2+ transients and its involvement in triggering the LLPS of the autophagy initiation complex FIP200 during autophagosome formation.
The researchers found that, under autophagy-inducing conditions, transient Ca2+ fluctuations occur on the ER surface. In response, CaMKIIβ dissociates from its bound actin filaments, forming punctate condensates, and becomes the site for FIP200 puncta formation.
Importantly, the study demonstrates that CaMKIIβ directly interacts with FIP200 and regulates the LLPS and physicochemical properties of the FIP200 complex through phosphorylation, thereby controlling the formation of autophagosomes.
Additionally, CaMKIIβ is revealed to involve in regulating the amplitude, duration, and propagation of ER Ca2+ transients during autophagy induction.
The researchers also highlighted that mutations in CaMKIIβ associated with neurodevelopmental disorders (such as MRD54) can disrupt autophagy, suggesting that abnormal autophagic activity may play a significant role in the onset and progression of these diseases.
"This study not only deepens our understanding of the autophagy initiation mechanism at the basic biological level, but also provides new insights and breakthroughs for potential therapeutic directions in autophagy regulation and diseases such as neurodevelopmental disorders," said Prof. ZHANG.
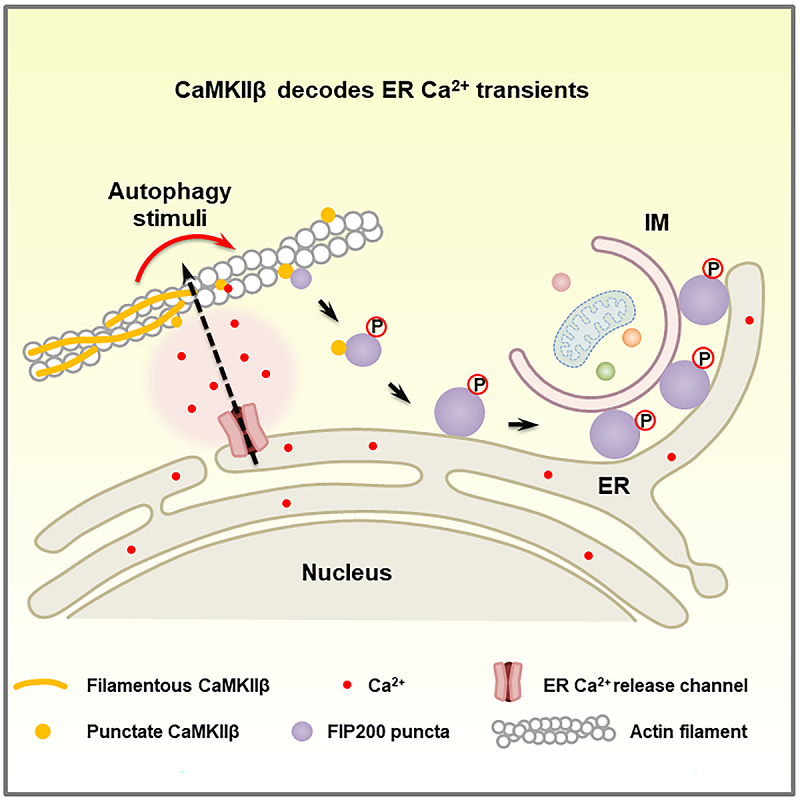
Figure. Model for the role of CaMKIIβ in transducing ER Ca2+ transients to autophagosome formation on the ER (Image by ZHANG Hong's group)
