Aberrant alveolar myofibroblasts (AMYFs) proliferation and differentiation are often associated with abnormal lung development and diseases such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. However, epigenetic mechanisms in regulating proliferation and differentiation of AMYFs remain poorly understood.
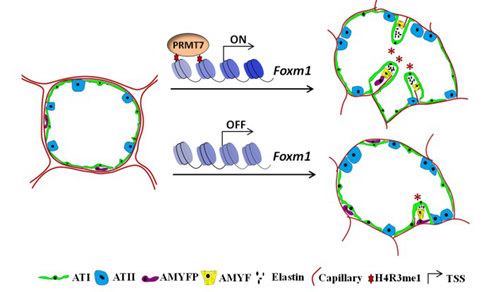
Prof. BAO Shilai's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported that protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7)-mediated histone arginine monomethylation activateed forkhead box M1 (Foxm1) transcriptional expression to regulate AMYFs proliferation and differentiation.
According to the researchers, PRMT7 is a critical molecule of AMYFs, and targeting PRMT7 may benefit AMYFs–associated pulmonary diseases therapy. Relevant results were published in
Cell Death & Disease on Sept. 8.
They investigated the function of PRMT7 through tissue-specific knockout mice model, and they found reduced AMYFs proliferation and differentiation, abnormal elastin deposition, and failure of alveolar septum formation in PRMT7-deficient mice.
They further showed that oncogene Foxm1 is a direct target of PRMT7 and that PRMT7-catelized monomethylation at histone H4 arginine 3 directly associate with chromatin of Foxm1 to suppress its transcription, and thereby down-regulation of cell-cycle-related genes to inhibit AMYFs proliferation and differentiation. Over-expression of Foxm1 in AMYFs significantly rescued PRMT7-deficiency-induced AMYFs proliferation and differentiation defects.
Since AMYFs are the primary cell types responsible for the accumulation of extracellular matrix during pulmonary diseases, these results suggest a promising approach of targeting PRMT7-mediated epigenetic modification for intervention of pulmonary diseases.
A proposed working model of PRMT7 for AMYFs proliferation and differentiation during lung alveolarization. (Image by IGDB)