
Newsroom
Scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently developed an ethanol-extraction surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) strategy for highly sensitive detection of poisons in oily matrix.
The strategy, proposed by researchers led by Prof. YANG Liangbao at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of CAS, can lead to great improvement in the detection of substances in oily matrix.
In recent years, poisonings occurred frequently in oily matrix, but due to the complex composition, it is difficult to quickly and directly detect the poisons in them.
"We used ethanol and other solvents to remove impurities in the oily matrix, and reduced the surface tension of the solution. In this way, the molecules can get close to the SERS substrate surface easily, so as to promote the target objects to enter the hot area of the SERS substrate," said Prof. YANG.
Combined with the hand-held Raman spectrometer, the research team performed SERS detection on paraquat and diquat in several common kitchen waste substrates.
"The detection limit could reach 10 ppb and 100 ppb, respectively," said Prof. YANG, "and the standard deviation is 7%. These data further proved that this method has good sensitivity and repeatability. It provides a solution to the problem of rapid detection of poisoning emergencies."
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Open Foundation of Beijing Field Material Evidence Testing Engineering Research Center, and the Science and Technology Strong Police Project of Anhui Province.
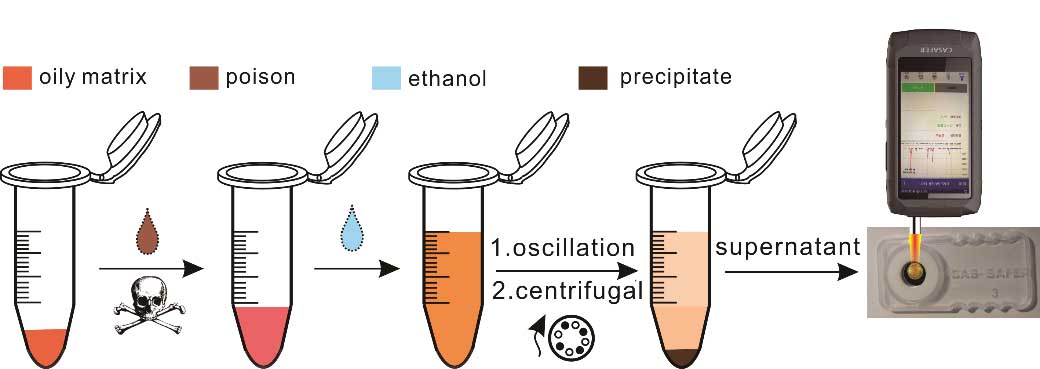
Schematic diagram of SERS detection based on ethanol extraction. (Image by WANG Yongtao)
