
Photocatalytic/Photoelectrocatalytic Inactivates Bacterial Cells
Oct 13, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Nowadays, human health is threatened by the waterborne pathogenic microbes such as bacteria and virus. The photocatalytic (PC) and photoelectrocatalytic (PEC) disinfection technique are extensively investigated due to their high efficiency, energy conservation and self-cleaning capacity. However, the biohazards inactivation mechanism of PC and PEC systems have not been well understood.
The researchers from Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ph.D candidate SUN Hongwei with his supervisors Prof. AN Taicheng and Prof. LI Guiying, made noticeable progress toward the in-depth understanding of PC and PEC disinfection mechanism, and a systematic approach was developed by tracking the decomposed building blocks with Escherichia coli K-12 as the model microorganism.
Their study demonstrated that the photogenerated reactive oxygen species (ROSs) was mainly responsible for the bacterial inactivation. In PEC system with immobilized catalyst, the dominant ROSs is H2O2. Whereas in the PC system with suspension catalyst, h+ and •OH were proved to be main bactericides. During the PC or PEC inactivation, the ROSs overwhelm the antioxidative capacity of bacterial protective enzymes, and then caused bacterial membrane damage, followed by leakage of cytoplasm substances. Especially, the oxidative damage and leakage of proteins and DNA was observed during PEC disinfection.
The work has been published in the journal “Environmental Science & Technology” (H.W. Sun, G.Y. Li, X. Nie, H.X. Shi, P.K. Wong, H.J. Zhao, T.C. An*, Systematic approach to in-depth understanding of photoelectrocatalytic bacterial inactivation mechanisms by tracking the decomposed building blocks. Environ Sci Technol 2014, 48 (16), 9412-9419.)
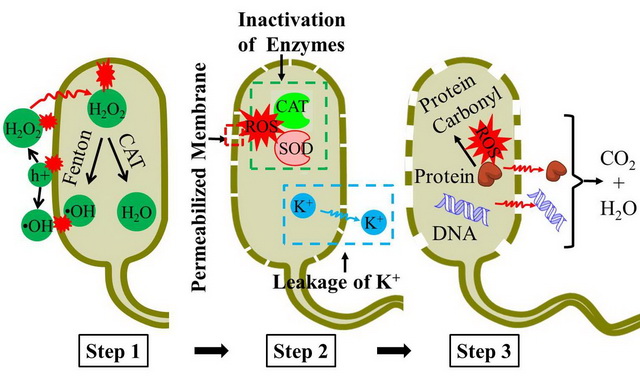
loss of cell membrane integrity and increased permeability, followed by the decomposition of cell envelope (Image by AN's research group)
Nowadays, human health is threatened by the waterborne pathogenic microbes such as bacteria and virus. The photocatalytic (PC) and photoelectrocatalytic (PEC) disinfection technique are extensively investigated due to their high efficiency, energy conservation and self-cleaning capacity. However, the biohazards inactivation mechanism of PC and PEC systems have not been well understood.
The researchers from Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ph.D candidate SUN Hongwei with his supervisors Prof. AN Taicheng and Prof. LI Guiying, made noticeable progress toward the in-depth understanding of PC and PEC disinfection mechanism, and a systematic approach was developed by tracking the decomposed building blocks with Escherichia coli K-12 as the model microorganism.
Their study demonstrated that the photogenerated reactive oxygen species (ROSs) was mainly responsible for the bacterial inactivation. In PEC system with immobilized catalyst, the dominant ROSs is H2O2. Whereas in the PC system with suspension catalyst, h+ and •OH were proved to be main bactericides. During the PC or PEC inactivation, the ROSs overwhelm the antioxidative capacity of bacterial protective enzymes, and then caused bacterial membrane damage, followed by leakage of cytoplasm substances. Especially, the oxidative damage and leakage of proteins and DNA was observed during PEC disinfection.
The work has been published in the journal “Environmental Science & Technology” (H.W. Sun, G.Y. Li, X. Nie, H.X. Shi, P.K. Wong, H.J. Zhao, T.C. An*, Systematic approach to in-depth understanding of photoelectrocatalytic bacterial inactivation mechanisms by tracking the decomposed building blocks. Environ Sci Technol 2014, 48 (16), 9412-9419.)

loss of cell membrane integrity and increased permeability, followed by the decomposition of cell envelope (Image by AN's research group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

