
Central Prolactin Receptors PRLRs Regulate Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity
Oct 09, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

A group of researchers led by Professor GUO Feifan from the Institute for Nutritional Sciences (INS), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences, has found that central prolactin receptors (PRLRs) regulate hepatic insulin resistance in mice via signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) and the vagus nerve.
The central nervous system (CNS), especially the hypothalamus, has been shown to be critical in the regulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity. PRLR, a type Ⅰcytokine receptor expressed in most oranges in mammals, has been reported to participate in the energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism by Dr. GUO and other investigators. However, whether hypothalamic PRLRs regulate peripheral insulin sensitivity remains unknown.
Research group led by Dr. GUO first generated adenoviruses expressing PRLR (Ad-PRLR) or shRNA directed against the PRLR (Ad-shPRLR), respectively. These adenoviruses were administered by intracerebroventricular (icv) injection into the third ventricle of mice. They found that activation of hypothalamic PRLR by Ad-PRLR improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in mice. Consistently, inhibition of PRLR in the hypothalamus by Ad-shPRLR results in reduced hepatic insulin sensitivity.
When exploring the mechanisms, the researchers found that signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) phosphorylaton was significantly upregulated by Ad-PRLR and downregulated by Ad-shPRLR Inhibition of STAT5 by icv injection of adenoviruses expressing shRNA directed against the STAT5 (Ad-shSTAT5) attenuated PRLR-improved hepatic insulin sensitivity. These data suggests an important role of hypothalamic STAT5 in the regulation of insulin sensitivity by PRLR.
Accumulating evidence showed that the hypothalamus regulates peripheral tissues through the autonomic nervous system and the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve provides the primary link between the hypothalamus and liver. They performed selective hepatic branch vagotomy or sham surgery in mice, followed by icv injection of Ad-PRLR and found that Ad-PRLR-improved insulin sensitivity was diminished by hepatic vagotomy. These results clarify the role of the vagus nerve in hypothalamic PRLR-regulated insulin sensitivity.
The group members observed that PRLR protein levels were downregulated significantly in the hypothalamus of db/db mice compared with wild-type mice. Over-expression of hypothalamic PRLR significantly ameliorates insulin resistance in db/db mice.
This study identifies a novel central pathway in regulating hepatic insulin sensitivity which is mediated by hypothalamic PRLR/STAT5 signaling and the vagus nerve and demonstrates an important role for hypothalamic PRLR under conditions of insulin resistance.
This work entitled “Central prolactin receptors (PRLRs) regulate hepatic insulin resistance in mice via signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) and the vagus nerve” has been published online before print in the Diabetologia in July, 2014.
This work was supported by research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Contact:
GUO Feifan, Ph.D., Principal Investigator
Institute for Nutritional Sciences, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Shanghai 200031, China.
Tel: 86-21-54920945;
Fax: 86-21-54920245;
E-mail: ffguo@sibs.ac.cn
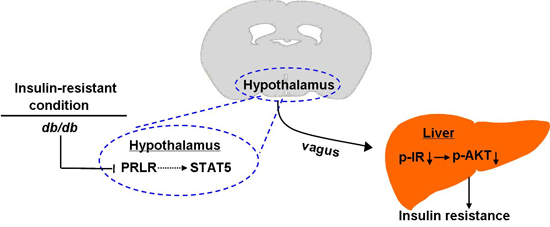
Figure: Central prolactin receptors (PRLRs) regulate hepatic insulin sensit (Image by Dr. GUO Feifan's group)
A group of researchers led by Professor GUO Feifan from the Institute for Nutritional Sciences (INS), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences, has found that central prolactin receptors (PRLRs) regulate hepatic insulin resistance in mice via signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) and the vagus nerve.
The central nervous system (CNS), especially the hypothalamus, has been shown to be critical in the regulation of peripheral insulin sensitivity. PRLR, a type Ⅰcytokine receptor expressed in most oranges in mammals, has been reported to participate in the energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism by Dr. GUO and other investigators. However, whether hypothalamic PRLRs regulate peripheral insulin sensitivity remains unknown.
Research group led by Dr. GUO first generated adenoviruses expressing PRLR (Ad-PRLR) or shRNA directed against the PRLR (Ad-shPRLR), respectively. These adenoviruses were administered by intracerebroventricular (icv) injection into the third ventricle of mice. They found that activation of hypothalamic PRLR by Ad-PRLR improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in mice. Consistently, inhibition of PRLR in the hypothalamus by Ad-shPRLR results in reduced hepatic insulin sensitivity.
When exploring the mechanisms, the researchers found that signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) phosphorylaton was significantly upregulated by Ad-PRLR and downregulated by Ad-shPRLR Inhibition of STAT5 by icv injection of adenoviruses expressing shRNA directed against the STAT5 (Ad-shSTAT5) attenuated PRLR-improved hepatic insulin sensitivity. These data suggests an important role of hypothalamic STAT5 in the regulation of insulin sensitivity by PRLR.
Accumulating evidence showed that the hypothalamus regulates peripheral tissues through the autonomic nervous system and the hepatic branch of the vagus nerve provides the primary link between the hypothalamus and liver. They performed selective hepatic branch vagotomy or sham surgery in mice, followed by icv injection of Ad-PRLR and found that Ad-PRLR-improved insulin sensitivity was diminished by hepatic vagotomy. These results clarify the role of the vagus nerve in hypothalamic PRLR-regulated insulin sensitivity.
The group members observed that PRLR protein levels were downregulated significantly in the hypothalamus of db/db mice compared with wild-type mice. Over-expression of hypothalamic PRLR significantly ameliorates insulin resistance in db/db mice.
This study identifies a novel central pathway in regulating hepatic insulin sensitivity which is mediated by hypothalamic PRLR/STAT5 signaling and the vagus nerve and demonstrates an important role for hypothalamic PRLR under conditions of insulin resistance.
This work entitled “Central prolactin receptors (PRLRs) regulate hepatic insulin resistance in mice via signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) and the vagus nerve” has been published online before print in the Diabetologia in July, 2014.
This work was supported by research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation and Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Contact:
GUO Feifan, Ph.D., Principal Investigator
Institute for Nutritional Sciences, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Shanghai 200031, China.
Tel: 86-21-54920945;
Fax: 86-21-54920245;
E-mail: ffguo@sibs.ac.cn

Figure: Central prolactin receptors (PRLRs) regulate hepatic insulin sensit (Image by Dr. GUO Feifan's group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

