
Researchers Reveal Emotional Valence Map in Limbic Forebrain
Sep 24, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Emotions color our lives and drive behaviors. Most emotions can be categorized along two dimensions: valence (value), ranging from negative to positive, and salience (arousal, intensity), ranging from weak to strong. Although great advances have been made toward understanding the sensory representations of the external world, how different emotional valences are represented in the brain has remained largely elusive.
To extract the valence representation of an emotion in the whole brain, Dr. HU Hailan’s lab devised a strategy to compare the activity patterns evoked by two emotional stimuli with contrasting valence (morphine, foot shock) in the same mouse brain, by modifying a double-labeling technique based on the distinct induction time course of the mRNA and protein signals of the Immediate Early Gene (IEG) gene c-fos. C-fos expression is generally low throughout the limbic nervous system in resting animals. Following neuronal activation, c-fos mRNA accumulates in minutes and decays in a couple hours, whereas its protein product appears slower and lasts much longer. Thus, when two stimuli are sequentially applied at an appropriate interval, neural circuits activated by the two stimuli can be represented by the c-fos protein and mRNA signals respectively, which in turn can be revealed by dual labeling using fluorescence immunohistochemistry (FIHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
Using the TAI-FISH dual labeling technique, they examined the c-fos activation patterns elicited by morphine and foot shock in the same mouse brain and found that morphine and foot shock evoked largely distinct neural ensembles throughout the limbic forebrain, despite activating many of the same regions. As morphine and foot shock have different sensory properties, they introduced additional pairs of emotional stimuli, including chocolate and restraint stress. In the nucleus accumbens (NAc), rewarding and aversive stimulus pairs (morphine/foot shock, morphine/restraint) recruited spatially intermingled neurons, whereas stimulus pairs of similar valence (morphine/chocolate, foot shock/restraint) activated largely overlapping neural groups, suggesting the existence of a functional valence map.
The results provide insights into the internal representation of emotional valences and the functional organization of NAc. In addition, with the new amplification step allowing better separation of IEG mRNA and protein signals, TAI-FISH provides a much-needed molecular imaging technique for mapping the neural representations of two distinct behaviors across the whole brain at single-cell resolution.
This research entitled “Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH” was published online in Nature Neuroscience on September 22, 2014. This work was mainly carried out by graduate students XIU Jianbo and ZHANG Qi under the supervision of Dr. HU Hailan, in collaboration with graduate students ZHOU Tao, ZHOU Tingting, and research assistant CHEN Yang.
The work was supported by the 973 Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the Outstanding Youth Program, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Hundreds of Talents Program.
Contact:
HU Hailan
Institute of Neuroscience, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Shanghai, China.
E-mail: hailan@ion.ac.cn
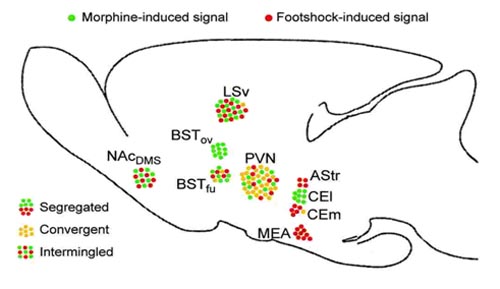
Figure 1: Summary of patterns of interaction between neural representations of morphine and foot shock in different regions of the limbic forebrain, as revealed by TAI-FISH (Image by Dr. HU Hailan)

Figure 2: The intermingled pattern of neurons encoding opposite valence in nucleus accumbens (Image by Dr. HU Hailan)
Emotions color our lives and drive behaviors. Most emotions can be categorized along two dimensions: valence (value), ranging from negative to positive, and salience (arousal, intensity), ranging from weak to strong. Although great advances have been made toward understanding the sensory representations of the external world, how different emotional valences are represented in the brain has remained largely elusive.
To extract the valence representation of an emotion in the whole brain, Dr. HU Hailan’s lab devised a strategy to compare the activity patterns evoked by two emotional stimuli with contrasting valence (morphine, foot shock) in the same mouse brain, by modifying a double-labeling technique based on the distinct induction time course of the mRNA and protein signals of the Immediate Early Gene (IEG) gene c-fos. C-fos expression is generally low throughout the limbic nervous system in resting animals. Following neuronal activation, c-fos mRNA accumulates in minutes and decays in a couple hours, whereas its protein product appears slower and lasts much longer. Thus, when two stimuli are sequentially applied at an appropriate interval, neural circuits activated by the two stimuli can be represented by the c-fos protein and mRNA signals respectively, which in turn can be revealed by dual labeling using fluorescence immunohistochemistry (FIHC) and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).
Using the TAI-FISH dual labeling technique, they examined the c-fos activation patterns elicited by morphine and foot shock in the same mouse brain and found that morphine and foot shock evoked largely distinct neural ensembles throughout the limbic forebrain, despite activating many of the same regions. As morphine and foot shock have different sensory properties, they introduced additional pairs of emotional stimuli, including chocolate and restraint stress. In the nucleus accumbens (NAc), rewarding and aversive stimulus pairs (morphine/foot shock, morphine/restraint) recruited spatially intermingled neurons, whereas stimulus pairs of similar valence (morphine/chocolate, foot shock/restraint) activated largely overlapping neural groups, suggesting the existence of a functional valence map.
The results provide insights into the internal representation of emotional valences and the functional organization of NAc. In addition, with the new amplification step allowing better separation of IEG mRNA and protein signals, TAI-FISH provides a much-needed molecular imaging technique for mapping the neural representations of two distinct behaviors across the whole brain at single-cell resolution.
This research entitled “Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH” was published online in Nature Neuroscience on September 22, 2014. This work was mainly carried out by graduate students XIU Jianbo and ZHANG Qi under the supervision of Dr. HU Hailan, in collaboration with graduate students ZHOU Tao, ZHOU Tingting, and research assistant CHEN Yang.
The work was supported by the 973 Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the Outstanding Youth Program, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Hundreds of Talents Program.
Contact:
HU Hailan
Institute of Neuroscience, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Shanghai, China.
E-mail: hailan@ion.ac.cn

Figure 1: Summary of patterns of interaction between neural representations of morphine and foot shock in different regions of the limbic forebrain, as revealed by TAI-FISH (Image by Dr. HU Hailan)

Figure 2: The intermingled pattern of neurons encoding opposite valence in nucleus accumbens (Image by Dr. HU Hailan)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

