
Insight into Electrocatalytically Active Sites in Fe/N/C catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Sep 11, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Fuel cells, as a clean and efficient power source, have attracted significant attention during the last decades. The cathodic oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is at the heart of fuel cell performance, and efficient ORR electrocatalysts are essential for practical applications. The cost of widely used platinum catalysts is prohibitive in fuel cells, so Fe/N/C non-precious metal catalysts with high ORR activity and stability become the potential candidates of Pt-based catalysts. The actual structures of active sites in Fe/N/C electrocatalysts remain elusive, because the Fe/N/C electrocatalysts are inherently highly heterogeneous and have complex structure.
Prof. SU Dangsheng and PhD student ZHU Yansong from Catalysis and Materials Devision (Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science) show for the first time the N6-coordination of the active Fe-N complexes confined in complex carbon-based electrocatalysts. The information is validated by combining advanced electron microscopy and Mössbauer spectroscopy methods. Taking account of the inherently highly heterogeneous and complex structure of the real Fe-N-containing electrocatalysts, they have excluded the likelihood of other iron-containing phases as ORR active sites, such as Fe3C or FeS. The related research results are published online on Angewandte Chemie International Edition (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201405314) in August.
The knowledge of the real active site FeN6 will lead the way to target-specific synthesis of highly active and stable Fe/N/C catalysts for ORR. The authors acknowledge the financial support from MOST (2011CBA00504), NSFC of China (21133010, 21203215, 51221264, 21261160487), and ‘Strategic Priority Research Program’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDA09030103.
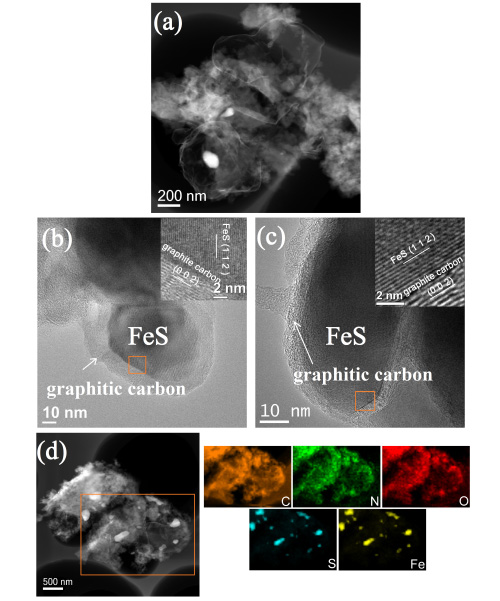

Figure 1 a) STEM image b) HRTEM image of PpPD-Fe-C c) HRTEM image d) HAADF-STEM maps of Fe-N-C (Image by IMR)
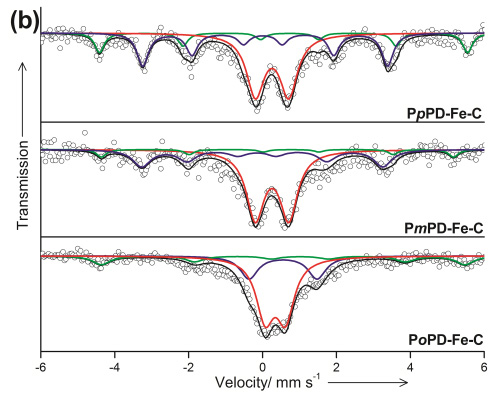
Figure 2 Mçssbauer spectra forFe-N-C (Image by IMR)
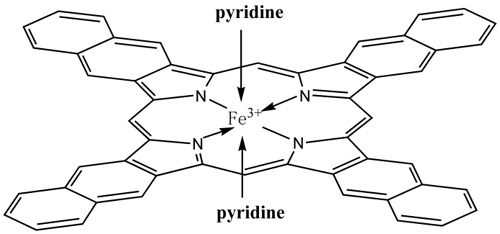
Figure 3 Iron complex structure (Image by IMR)
Fuel cells, as a clean and efficient power source, have attracted significant attention during the last decades. The cathodic oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is at the heart of fuel cell performance, and efficient ORR electrocatalysts are essential for practical applications. The cost of widely used platinum catalysts is prohibitive in fuel cells, so Fe/N/C non-precious metal catalysts with high ORR activity and stability become the potential candidates of Pt-based catalysts. The actual structures of active sites in Fe/N/C electrocatalysts remain elusive, because the Fe/N/C electrocatalysts are inherently highly heterogeneous and have complex structure.
Prof. SU Dangsheng and PhD student ZHU Yansong from Catalysis and Materials Devision (Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science) show for the first time the N6-coordination of the active Fe-N complexes confined in complex carbon-based electrocatalysts. The information is validated by combining advanced electron microscopy and Mössbauer spectroscopy methods. Taking account of the inherently highly heterogeneous and complex structure of the real Fe-N-containing electrocatalysts, they have excluded the likelihood of other iron-containing phases as ORR active sites, such as Fe3C or FeS. The related research results are published online on Angewandte Chemie International Edition (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201405314) in August.
The knowledge of the real active site FeN6 will lead the way to target-specific synthesis of highly active and stable Fe/N/C catalysts for ORR. The authors acknowledge the financial support from MOST (2011CBA00504), NSFC of China (21133010, 21203215, 51221264, 21261160487), and ‘Strategic Priority Research Program’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDA09030103.

Figure 1 a) STEM image b) HRTEM image of PpPD-Fe-C c) HRTEM image d) HAADF-STEM maps of Fe-N-C (Image by IMR)

Figure 2 Mçssbauer spectra forFe-N-C (Image by IMR)

Figure 3 Iron complex structure (Image by IMR)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

