
Function and Mechanism of "Bridge" between Aminoacylation Domain and Editing Domain of Human Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase Revealed
Aug 06, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Leucyl-tRNA synthetases (LeuRSs) catalyze the ester of leucine to its cognate tRNALeu. Leucine, isoleucine, methionine and novaline are similar in structure. Discrimination between cognate and non-cognate amino acids is inefficient for LeuRS. To improve the fidelity of catalyze reaction, the proofreading domain evolved to hydrolyze either misactivated aa-AMPs (pre-transfer editing) or mischarged tRNAs (post-transfer editing). The bridge between the catalysis domain and the editing domain is CP hairpin. It’s thought that the CP hairpin may maintain the correct conformation of LeuRS and involve the conformation change during catalysis. However, the details are still unknown.
The researchers from professor WANG Enduo’s group at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences deleted the CP1 hairpin domain of human cytoplasm leucyl-tRNA synthetase. The amino acid activation and the aminoacylation of LeuRS totally destroy. The tRNA binding affinity decline a lot. However the editing is almost intact. Chimera from archaea, prokaryote and eukaryote reveal that only the CP1 hairpin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae LeuRS (ScLeuRS) could partly rescue the hcLeuRS functions. The flexible residues in this domain may involve in the conformation change during enzyme catalysis. The polar residues may contribute to the affinity of tRNA binding.
This result could help understand the mechanism of leucyl-tRNA synthetase and find the different of leucyl-tRNA synthetases between human and pathogenic bacteria to design novel antibiotics.
This work entitled “A bridge between the aminoacylation and editing domains of leucyl-tRNA synthetase is crucial for its synthetic activity” was published online in RNA on July 22, 2014.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Basic Research Foundation of China and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
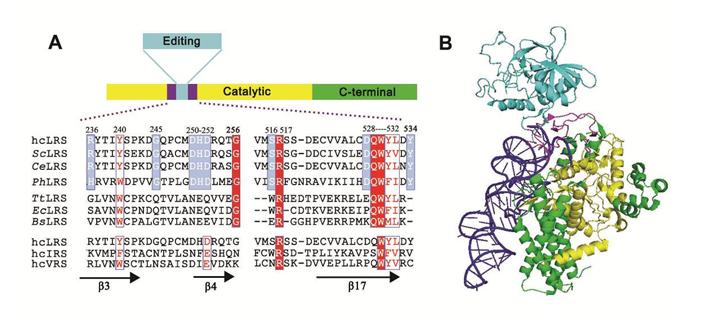
The location of CP hairpin domain in the 1st sequence and the 3rd structure of leucyl-tRNA synthetase. (Image by WANG Enduo`s group)
Leucyl-tRNA synthetases (LeuRSs) catalyze the ester of leucine to its cognate tRNALeu. Leucine, isoleucine, methionine and novaline are similar in structure. Discrimination between cognate and non-cognate amino acids is inefficient for LeuRS. To improve the fidelity of catalyze reaction, the proofreading domain evolved to hydrolyze either misactivated aa-AMPs (pre-transfer editing) or mischarged tRNAs (post-transfer editing). The bridge between the catalysis domain and the editing domain is CP hairpin. It’s thought that the CP hairpin may maintain the correct conformation of LeuRS and involve the conformation change during catalysis. However, the details are still unknown.
The researchers from professor WANG Enduo’s group at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences deleted the CP1 hairpin domain of human cytoplasm leucyl-tRNA synthetase. The amino acid activation and the aminoacylation of LeuRS totally destroy. The tRNA binding affinity decline a lot. However the editing is almost intact. Chimera from archaea, prokaryote and eukaryote reveal that only the CP1 hairpin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae LeuRS (ScLeuRS) could partly rescue the hcLeuRS functions. The flexible residues in this domain may involve in the conformation change during enzyme catalysis. The polar residues may contribute to the affinity of tRNA binding.
This result could help understand the mechanism of leucyl-tRNA synthetase and find the different of leucyl-tRNA synthetases between human and pathogenic bacteria to design novel antibiotics.
This work entitled “A bridge between the aminoacylation and editing domains of leucyl-tRNA synthetase is crucial for its synthetic activity” was published online in RNA on July 22, 2014.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Basic Research Foundation of China and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.

The location of CP hairpin domain in the 1st sequence and the 3rd structure of leucyl-tRNA synthetase. (Image by WANG Enduo`s group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

