
Genetic Diversity, Genetic Structure and Demographic History of Cycas Simplicipinna (Cycadaceae) Assessed by DNA Sequences and SSR Markers
Aug 01, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Cycas simplicipinna (T. Smitinand) K. Hill., belonging to Cycas (Cycadaceae), is a rare and endangered species in China. All cycads have been given the ‘First Grade’ conservation status in China. GONG Xun’s Group, from Kunming Institute of Botany (KIB), has made many in-depth researches on conservation genetics of Cycas for recent years, and some significant contributions have also been made on the protection of some Cycas plants.
Recently, under the guidance of Profs. GONG Xun and WANG Yuehua (Yunnan University), Dr. FENG Xiuyan from Kunming Institute of Botany used sequence data from two maternally inherited cpDNA and one biparentally inherited nuclear DNA (ITS4-ITS5) and sixteen biparentally inherited nuclear SSR loci to investigate genetic diversity, genetic structure and demographic history of seven collected populations of C. simplicipinna.
The main findings are as follows: 1) The species shows high genetic diversity at the species level, while low genetic diversity within the seven populations and high genetic differentiation among the populations. 2) There is a clear genetic structure within populations of C. simplicipinna, while no significant phylogeographical structure has been detected. 3) The population demography of C. simplicipinna was stable in history until approximately 50,000 years ago, at which time a contraction event occurred without an expansion later. Most haplotypes of C. simplicipinna were diverged during Pleistocene. 4) Bottleneck analysis showed that C. simplicipinna did not experience a recent severe bottleneck but underwent a past reduction in effective population size. The results derived from DNA sequences are consistent with the results inferred from SSR data.
In addition, estimates of effective population sizes based on SSR data indicated that the effective population size of only LUA and NBH was more than 100, and the size was less than 50 in three other investigated populations. Therefore, basing on the above research results, a reasonable and effective protection strategy for Cycas simplicipinna was proposed. This study also provides insights and guidelines for researching other Cycas species.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan United Foundation (U1136602). This manuscript entitled ‘Genetic diversity, genetic structure and demographic history of Cycas simplicipinna (Cycadaceae) assessed by DNA sequences and SSR markers’ was published on BMC Plant Biology on July 12, 2014.
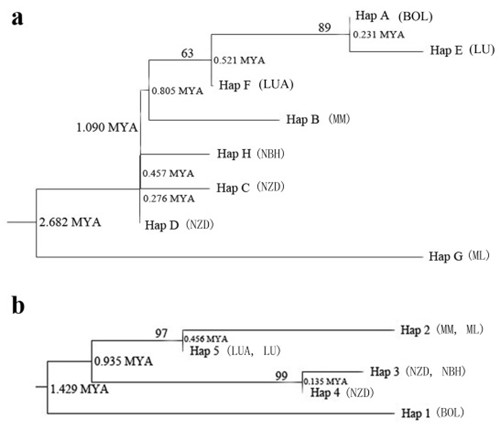
The divergence time of haplotypes of C. simplicipinna based on cpDNA (a) and nrDNA (b) (Image by KIB)
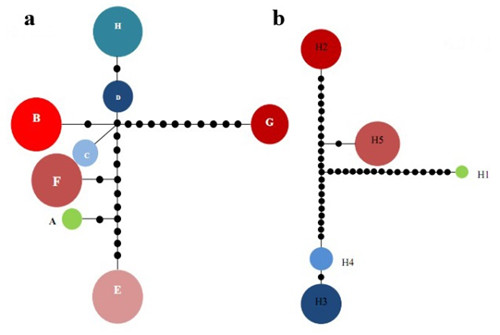
Network of haplotypes of C. simplicipinna based on cpDNA (a) and nrDNA (b) (Image by KIB)
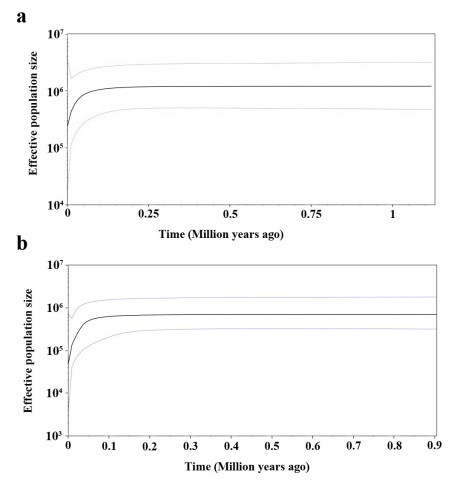
Bayesian skyline plot based on cpDNA (a) and nrDNA (b) for the effective population size fluctuation throughout time. (Image by KIB)
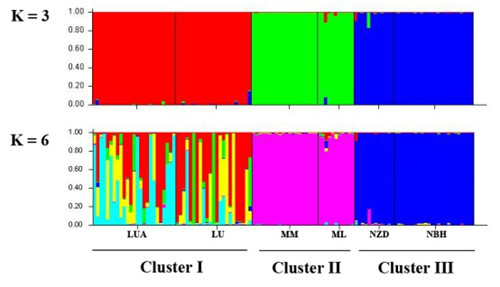
Estimated genetic clustering (K = 3 and 6) obtained with the STRUCTURE program for six populations of C. simplicipinna based on SSR data (Image by KIB)
Cycas simplicipinna (T. Smitinand) K. Hill., belonging to Cycas (Cycadaceae), is a rare and endangered species in China. All cycads have been given the ‘First Grade’ conservation status in China. GONG Xun’s Group, from Kunming Institute of Botany (KIB), has made many in-depth researches on conservation genetics of Cycas for recent years, and some significant contributions have also been made on the protection of some Cycas plants.
Recently, under the guidance of Profs. GONG Xun and WANG Yuehua (Yunnan University), Dr. FENG Xiuyan from Kunming Institute of Botany used sequence data from two maternally inherited cpDNA and one biparentally inherited nuclear DNA (ITS4-ITS5) and sixteen biparentally inherited nuclear SSR loci to investigate genetic diversity, genetic structure and demographic history of seven collected populations of C. simplicipinna.
The main findings are as follows: 1) The species shows high genetic diversity at the species level, while low genetic diversity within the seven populations and high genetic differentiation among the populations. 2) There is a clear genetic structure within populations of C. simplicipinna, while no significant phylogeographical structure has been detected. 3) The population demography of C. simplicipinna was stable in history until approximately 50,000 years ago, at which time a contraction event occurred without an expansion later. Most haplotypes of C. simplicipinna were diverged during Pleistocene. 4) Bottleneck analysis showed that C. simplicipinna did not experience a recent severe bottleneck but underwent a past reduction in effective population size. The results derived from DNA sequences are consistent with the results inferred from SSR data.
In addition, estimates of effective population sizes based on SSR data indicated that the effective population size of only LUA and NBH was more than 100, and the size was less than 50 in three other investigated populations. Therefore, basing on the above research results, a reasonable and effective protection strategy for Cycas simplicipinna was proposed. This study also provides insights and guidelines for researching other Cycas species.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan United Foundation (U1136602). This manuscript entitled ‘Genetic diversity, genetic structure and demographic history of Cycas simplicipinna (Cycadaceae) assessed by DNA sequences and SSR markers’ was published on BMC Plant Biology on July 12, 2014.

The divergence time of haplotypes of C. simplicipinna based on cpDNA (a) and nrDNA (b) (Image by KIB)

Network of haplotypes of C. simplicipinna based on cpDNA (a) and nrDNA (b) (Image by KIB)

Bayesian skyline plot based on cpDNA (a) and nrDNA (b) for the effective population size fluctuation throughout time. (Image by KIB)

Estimated genetic clustering (K = 3 and 6) obtained with the STRUCTURE program for six populations of C. simplicipinna based on SSR data (Image by KIB)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

