
Structural Analysis Reveals a Fundamental Mechanism Vital for Phospholipid Biosynthesis
Jul 10, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

A research team led by Professor LIU Zhenfeng at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences described the first structure of the CDP-DAG synthetase from Thermotoga maritima (TmCdsA) at 3.4 Å resolution.
Cytidine-diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG) synthetase, found extensively in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, is an important enzyme in the de novo synthesis of anionic phospholipid molecules with various head groups, including phosphatidyl inositol (PI), phosphatidyl glycerol (PG) and phosphatidyl serine (PS).
In Drosophila and zebra fish, Cds has a central role in phototransduction and vascular morphogenesis by controlling the availability of phosphoinositide 4,5 biphosphate (PIP2) through the phosphoinositide-recycling pathway. Knockout of Cds homologs impaired the biosynthesis of PG which is an essential lipid for the proper functioning of photosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria.
Professor LIU’s group found that TmCdsA forms a homodimerin both crystal and solution, and each monomer contains nine transmembrane helices arranged into three individual domains. The structure of TmCdsA represents a novel protein fold that is discovered for the first time. With a funnel-shaped cavity penetrating half way into the membrane, this integral membrane enzyme forms dual gateways to accept hydrophilic substrate (CTP/dCTP) from cytoplasm and hydrophobic substrate (phosphatidic acid) from membrane simultaneously. The researchers demonstrated that the catalytic center of TmCdsA is a Mg2+-K+ hetero-di-metal center located at the bottom of the cavity and coordinated by a conserved Asp-Asp dyad. These discoveries suggest a two-metal-ion catalytic mechanism for the Cds-mediated synthesis of CDP-DAG at the membrane-cytoplasm interface.
The work entitled “Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis” was published in Nature communications on June 27, 2014.
This project is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
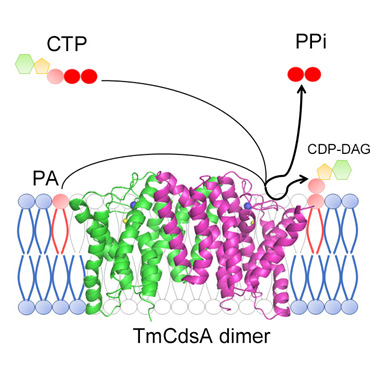
A cartoon model dissecting the structure of TmCdsA and the kinetic processes of the chemical reaction catalyzed by TmCdsA. From LIU Zhenfeng et.al.
A research team led by Professor LIU Zhenfeng at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences described the first structure of the CDP-DAG synthetase from Thermotoga maritima (TmCdsA) at 3.4 Å resolution.
Cytidine-diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG) synthetase, found extensively in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, is an important enzyme in the de novo synthesis of anionic phospholipid molecules with various head groups, including phosphatidyl inositol (PI), phosphatidyl glycerol (PG) and phosphatidyl serine (PS).
In Drosophila and zebra fish, Cds has a central role in phototransduction and vascular morphogenesis by controlling the availability of phosphoinositide 4,5 biphosphate (PIP2) through the phosphoinositide-recycling pathway. Knockout of Cds homologs impaired the biosynthesis of PG which is an essential lipid for the proper functioning of photosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria.
Professor LIU’s group found that TmCdsA forms a homodimerin both crystal and solution, and each monomer contains nine transmembrane helices arranged into three individual domains. The structure of TmCdsA represents a novel protein fold that is discovered for the first time. With a funnel-shaped cavity penetrating half way into the membrane, this integral membrane enzyme forms dual gateways to accept hydrophilic substrate (CTP/dCTP) from cytoplasm and hydrophobic substrate (phosphatidic acid) from membrane simultaneously. The researchers demonstrated that the catalytic center of TmCdsA is a Mg2+-K+ hetero-di-metal center located at the bottom of the cavity and coordinated by a conserved Asp-Asp dyad. These discoveries suggest a two-metal-ion catalytic mechanism for the Cds-mediated synthesis of CDP-DAG at the membrane-cytoplasm interface.
The work entitled “Structure and mechanism of an intramembrane liponucleotide synthetase central for phospholipid biosynthesis” was published in Nature communications on June 27, 2014.
This project is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.

A cartoon model dissecting the structure of TmCdsA and the kinetic processes of the chemical reaction catalyzed by TmCdsA. From LIU Zhenfeng et.al.
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

