
Acid-resistant Magnetic Adsorbent Developed for Cr(VI)-containing Acidic Wastewater Treatment
Jul 03, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

The presence of Cr(VI) in industrial wastewaters from electroplating, chromic salts industry, leather tanning and pigment manufacture is a potential hazard to the public health and ecological systems due to its mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. Therefore, it is urgent to clear Cr(VI) from wastewater to meet emission standard before discharging into the environment.
Currently, magnetic separation has become one of the promising techniques for environmental purification. However, the most widely used magnetic adsorbents are based on iron oxides and it tends to be dissolved in acidic wastewater. Therefore, exploring a magnetic adsorbent with good acid resistance and adsorption properties is a goal of general concern.
The research team led by Prof. LIU Huizhou at Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed novel amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2@cellulose composite material. This material showed a high acid resistance and could long-termly exist in an aqueous solution at a pH of 2.0. Besides, it exhibited a high magnetic responsiveness (the saturation magnetization: 10.1 emu/g), suggesting that it could be easily and quickly separated from a suspension by applying an external magnetic field (Fig. 1).
The adsorption results demonstrated that this material showed a high adsorption capacity and a rapid adsorption rate, with the maximum adsorption capacity and equilibrium time of 171.5 mg/g and 10 min, respectively. The regeneration study revealed that the adsorbent has a good reusability, and the adsorption mechanism was electrostatic attraction (Fig. 2).
In conclusion, the magnetic cellulose composite material should be a promising adsorbent for Cr(VI) removal. These achievements laid a foundation for high efficient magnetic separation of Cr(VI) from acidic wastewater and published in Chemical Engineering Journal (2014, 241: 175-183).

Fig. 1 The magnetic separation process of Cr(VI) from wastewater (Image by IPE)
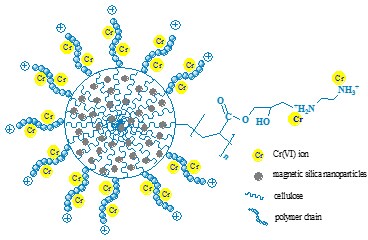
Fig. 2 The schematic diagram of electrostatic interaction (Image by IPE)
The presence of Cr(VI) in industrial wastewaters from electroplating, chromic salts industry, leather tanning and pigment manufacture is a potential hazard to the public health and ecological systems due to its mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. Therefore, it is urgent to clear Cr(VI) from wastewater to meet emission standard before discharging into the environment.
Currently, magnetic separation has become one of the promising techniques for environmental purification. However, the most widely used magnetic adsorbents are based on iron oxides and it tends to be dissolved in acidic wastewater. Therefore, exploring a magnetic adsorbent with good acid resistance and adsorption properties is a goal of general concern.
The research team led by Prof. LIU Huizhou at Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed novel amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2@cellulose composite material. This material showed a high acid resistance and could long-termly exist in an aqueous solution at a pH of 2.0. Besides, it exhibited a high magnetic responsiveness (the saturation magnetization: 10.1 emu/g), suggesting that it could be easily and quickly separated from a suspension by applying an external magnetic field (Fig. 1).
The adsorption results demonstrated that this material showed a high adsorption capacity and a rapid adsorption rate, with the maximum adsorption capacity and equilibrium time of 171.5 mg/g and 10 min, respectively. The regeneration study revealed that the adsorbent has a good reusability, and the adsorption mechanism was electrostatic attraction (Fig. 2).
In conclusion, the magnetic cellulose composite material should be a promising adsorbent for Cr(VI) removal. These achievements laid a foundation for high efficient magnetic separation of Cr(VI) from acidic wastewater and published in Chemical Engineering Journal (2014, 241: 175-183).

Fig. 1 The magnetic separation process of Cr(VI) from wastewater (Image by IPE)

Fig. 2 The schematic diagram of electrostatic interaction (Image by IPE)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

