
SIA Researchers Conducted Comparative Study on EMG Pattern Recognition for Anthropomorphic Robotic Hand
Jul 01, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Nowadays, prosthetic devices have helped many disabled people who have lost limbs to deal with their daily life. Advanced commercial prosthetic hand such as Otto Bock hand, i-Limb hand, and Smart hand have been able to achieve some motions like human hands. The approach using electromyography (EMG) signals from amputee persons’ remnant muscles to control prosthetic devices is beneficial to restore the missing functionality of amputated limbs, and it has a history of about 40 years.
In an EMG pattern recognition system, feature extraction is the process that converts original sEMG signals to a compact and informative set of features. Traditional methods such as time-domain and frequency-domain analyzing methods have been widely used in EMG pattern recognition and they have a good capability to track muscular changes. However, these methods are not effective in detecting the critical feature of sEMG signals during transient human movements. In order to recognize more motion patterns, more channels of sEMG singles and more kinds of features are used to increase the information extracted from sEMG signals.
Recently, rearchers from Shenyang Institute of Automation have conducted a study on EMG pattern recognition based on principal component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) for an anthropomorphic robotic hand. In this study, the pattern recognition system consists of the feature extraction including five kinds of analysis methods, PCA feature projection, LDA feature projection and minimum distance classifier (MDC), as shown in Fig. 1. Nine kinds of hand/wrist motions were selected, and four channels of sEMG signals from human’s forearm were collected.
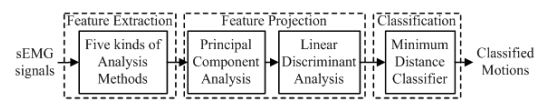
Fig. 1. Block diagram of EMG pattern recognition system. (Image by ZHANG Daohui et.al)
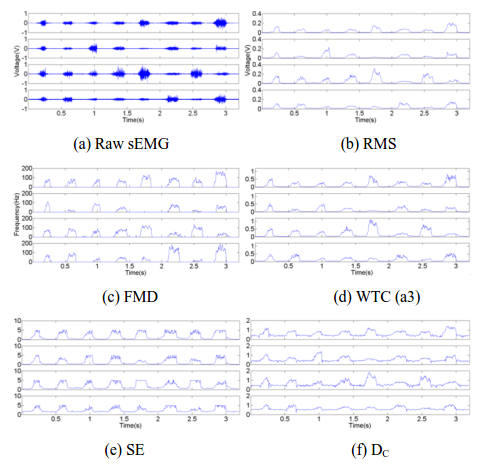
Fig. 2. Some features extracted from 4 channels of sEMG signals. (Image by ZHANG Daohui et.al)
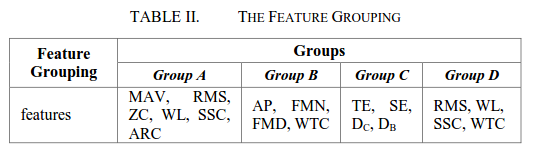
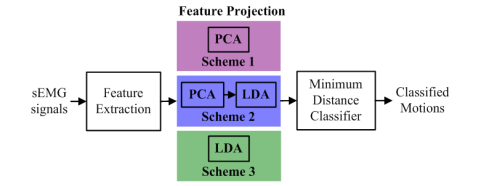
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the three feature projection schemes. (Image by ZHANG Daohui et.al)
Experimental results indicated that PCA+LDA projection didn’t improve the recognition performance much compared to LDA projection, and the time-domain features and wavelet transform features were able to obtain a better performance on both the classification accuracy and the processing time compared to the frequency-domain features, nonlinear entropy features and fractal analysis features.
This work was presented at the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation (ICRA) which was held in Hong Kong during May 31 to June 7, 2014.
Contact:
ZHANG Daohui
zhangdaohui@sia.cn
Shenyang Institute of Automation
Nowadays, prosthetic devices have helped many disabled people who have lost limbs to deal with their daily life. Advanced commercial prosthetic hand such as Otto Bock hand, i-Limb hand, and Smart hand have been able to achieve some motions like human hands. The approach using electromyography (EMG) signals from amputee persons’ remnant muscles to control prosthetic devices is beneficial to restore the missing functionality of amputated limbs, and it has a history of about 40 years.
In an EMG pattern recognition system, feature extraction is the process that converts original sEMG signals to a compact and informative set of features. Traditional methods such as time-domain and frequency-domain analyzing methods have been widely used in EMG pattern recognition and they have a good capability to track muscular changes. However, these methods are not effective in detecting the critical feature of sEMG signals during transient human movements. In order to recognize more motion patterns, more channels of sEMG singles and more kinds of features are used to increase the information extracted from sEMG signals.
Recently, rearchers from Shenyang Institute of Automation have conducted a study on EMG pattern recognition based on principal component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) for an anthropomorphic robotic hand. In this study, the pattern recognition system consists of the feature extraction including five kinds of analysis methods, PCA feature projection, LDA feature projection and minimum distance classifier (MDC), as shown in Fig. 1. Nine kinds of hand/wrist motions were selected, and four channels of sEMG signals from human’s forearm were collected.

Fig. 1. Block diagram of EMG pattern recognition system. (Image by ZHANG Daohui et.al)

Fig. 2. Some features extracted from 4 channels of sEMG signals. (Image by ZHANG Daohui et.al)


Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the three feature projection schemes. (Image by ZHANG Daohui et.al)
Experimental results indicated that PCA+LDA projection didn’t improve the recognition performance much compared to LDA projection, and the time-domain features and wavelet transform features were able to obtain a better performance on both the classification accuracy and the processing time compared to the frequency-domain features, nonlinear entropy features and fractal analysis features.
This work was presented at the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation (ICRA) which was held in Hong Kong during May 31 to June 7, 2014.
Contact:
ZHANG Daohui
zhangdaohui@sia.cn
Shenyang Institute of Automation
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

