
3D Visual Experience Oriented Cross-layer Optimized Scalable Texture Plus Depth Based 3D Video Streaming to Improve 3D Visual Experience over Wireless Networks
Jun 24, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

With rapid progress in 3D video processing technology, 3D video will gradually move into home from the cinema by enabling 3DTV. Especially, with more advanced mobile 3D display devices, 3D video service will be one of the major traffic forms over the future wireless networks. Since mobile 3D video can provide the “anywhere, anytime and any device” 3D visual experience, it will bring various novel media services such as mobile 3DTV, mobile 3D game and mobile 3D photo.
In current stage, the bandwidth of today’s wireless communication can already afford 3D video transmission. Since the 3D data format of texture video plus depth requires lower bandwidth than other formats, it is suitable for mobile application. However, the particular features of wireless network, such as limited bandwidth for multiple users, error-prone, time-varying channel quality and movable data receiving terminal, make the high performance wireless video streaming very challengeable. Compared with 2D video, the increased data amount and the particular 3D data characteristics make the 3D video transmission more challengeable. When the 3D video is transmitted over the wireless channel, the wireless networking technologies are very important for optimizing 3D video streaming performance. Due to the particular 3D video characteristics, some conventional 2D video streaming optimization technologies cannot work very efficiently for 3D video streaming. Hence, the advanced 3D video streaming technologies should be further developed.
Researchers from the Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Zhejiang Wanli University (Ningbo) cooperate to propose a 3D visual experience oriented cross-layer optimized scalable texture plus depth based 3D video streaming method to improve the 3D visual experience of the receiver.
By systematically considering the application layer video/depth/FEC bit-rate allocation, MAC layer multi-channel priorities, and physical layer modulation and channel coding scheme and the different protocol layer parameters are cross-layer optimized for 3D video streaming. In the cross-layer optimization, a networking-related 3D visual experience (3DVE) model which fuses the overlapped retinal view visual quality and depth sensation with mimicking human vision system is established to predict the 3D visual experience under the parameter configurations of different protocol layers.
Objective and subjective evaluation results indicate that the proposed 3D visual experience oriented cross-layer optimized scalable texture plus depth based 3D video streaming method can obtain superior 3D visual experience quality to the MSE (mean squired error) based cross-layer optimization method (see Fig.1 and Fig. 2).
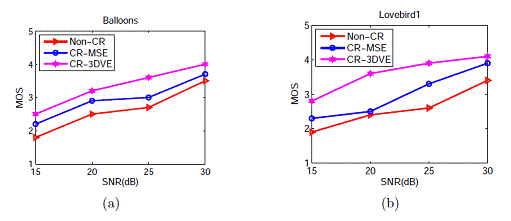
Fig.1 3D video streaming performances for different streaming schemes under different SNR values (Non-CR: non-cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming, CR-MSE: MSE-based (CR-MSE) cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming, CR-3DVE:3DVE oriented cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming) (Image by LIU)
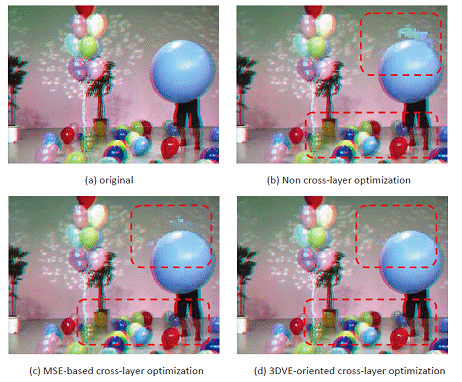
Fig.2 The 3D visual quality comparison between non-cross-layer optimized, MSE-based cross-layer optimized, and the 3DVE oriented cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming schemes at the 93th frame with the red-cyan color anaglyph format (Image by LIU)
This research was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos.61102077 and 11161140319, Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Contract LY13F010012, Public welfare projects of Zhejiang Province under Contract 2014C31072, and NSF under Grant nos.1145596 and 0830493.
References:
LIU Jinxia, LIU Yanwei, CI Song, YE Yun and YAO Ruixiao. 3D Visual Experience Oriented Cross-layer Optimized Scalable Texture plus Depth based 3D Video Streaming over Wireless Networks. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation (Vol.25, No. 5, pp.1209-1221, July 2014).
Contact:
LIU Yanwei
High Performance Network Laboratory, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
E-mail: liuyw@hpnl.ac.cn
With rapid progress in 3D video processing technology, 3D video will gradually move into home from the cinema by enabling 3DTV. Especially, with more advanced mobile 3D display devices, 3D video service will be one of the major traffic forms over the future wireless networks. Since mobile 3D video can provide the “anywhere, anytime and any device” 3D visual experience, it will bring various novel media services such as mobile 3DTV, mobile 3D game and mobile 3D photo.
In current stage, the bandwidth of today’s wireless communication can already afford 3D video transmission. Since the 3D data format of texture video plus depth requires lower bandwidth than other formats, it is suitable for mobile application. However, the particular features of wireless network, such as limited bandwidth for multiple users, error-prone, time-varying channel quality and movable data receiving terminal, make the high performance wireless video streaming very challengeable. Compared with 2D video, the increased data amount and the particular 3D data characteristics make the 3D video transmission more challengeable. When the 3D video is transmitted over the wireless channel, the wireless networking technologies are very important for optimizing 3D video streaming performance. Due to the particular 3D video characteristics, some conventional 2D video streaming optimization technologies cannot work very efficiently for 3D video streaming. Hence, the advanced 3D video streaming technologies should be further developed.
Researchers from the Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Zhejiang Wanli University (Ningbo) cooperate to propose a 3D visual experience oriented cross-layer optimized scalable texture plus depth based 3D video streaming method to improve the 3D visual experience of the receiver.
By systematically considering the application layer video/depth/FEC bit-rate allocation, MAC layer multi-channel priorities, and physical layer modulation and channel coding scheme and the different protocol layer parameters are cross-layer optimized for 3D video streaming. In the cross-layer optimization, a networking-related 3D visual experience (3DVE) model which fuses the overlapped retinal view visual quality and depth sensation with mimicking human vision system is established to predict the 3D visual experience under the parameter configurations of different protocol layers.
Objective and subjective evaluation results indicate that the proposed 3D visual experience oriented cross-layer optimized scalable texture plus depth based 3D video streaming method can obtain superior 3D visual experience quality to the MSE (mean squired error) based cross-layer optimization method (see Fig.1 and Fig. 2).

Fig.1 3D video streaming performances for different streaming schemes under different SNR values (Non-CR: non-cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming, CR-MSE: MSE-based (CR-MSE) cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming, CR-3DVE:3DVE oriented cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming) (Image by LIU)

Fig.2 The 3D visual quality comparison between non-cross-layer optimized, MSE-based cross-layer optimized, and the 3DVE oriented cross-layer optimized 3D video streaming schemes at the 93th frame with the red-cyan color anaglyph format (Image by LIU)
This research was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos.61102077 and 11161140319, Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Contract LY13F010012, Public welfare projects of Zhejiang Province under Contract 2014C31072, and NSF under Grant nos.1145596 and 0830493.
References:
LIU Jinxia, LIU Yanwei, CI Song, YE Yun and YAO Ruixiao. 3D Visual Experience Oriented Cross-layer Optimized Scalable Texture plus Depth based 3D Video Streaming over Wireless Networks. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation (Vol.25, No. 5, pp.1209-1221, July 2014).
Contact:
LIU Yanwei
High Performance Network Laboratory, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
E-mail: liuyw@hpnl.ac.cn
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

