
A Thermophilic Strain Isolated for Efficient Lactic Acid Production from Wheat Straw
Jun 23, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Lactic acid is an important chemical with versatile applications in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. Recent demands for lactic acid have surged due to the increasing manufacture of environment-friendly poly lactic acid. During the production of lactic acid by fermentation, the cost of the carbon source is very significant. Hence, lignocellulosic materials are regarded as suitable feedstocks for lactic acid production. However, due to the limitation of strain, the process of lactic acid production from lignocellulose is usually divided into individual operating units, including biomass pretreatment, hemicellulosic hydrolysates detoxification and fermentation, cellulose saccharification and fermentation. The separated operations make the overall process inefficient and thus the commercial production of lactic acid from lignocellulose is uneconomical.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. WAN Yinhua at Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences isolated a thermophilic lactic acid producer, Bacillus coagulans strain IPE22. With this strain, an efficient process was also developed for lactic acid production from wheat straw.
B. coagulans IPE22 showed remarkable capability to ferment pentose, hexose and cellobiose at temperature above 50°C, and was also resistant to inhibitors from lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Based on the strain’s promising features, an efficient process was developed to produce lactic acid from wheat straw. The process consisted of biomass pretreatment by dilute sulfuric acid and subsequent SSCF (simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation). The operations of solid-liquid separation and detoxification were avoided, and the slurry of pretreated wheat straw was directly fermented. Using this process, 46.12 g lactic acid could be produced from 100 g dry wheat straw with 20 FPU (filter paper activity units)/g cellulose and 10 g/L corn steep liquid powder as nitrogen source. The process by B. coagulans IPE22 provides an economical route to produce lactic acid from lignocellulose.
This work has been published in Bioresource Technology, 2014, 158: 396-399.

(a) SEM image of B. coagulans IPE22; (Image by IPE)
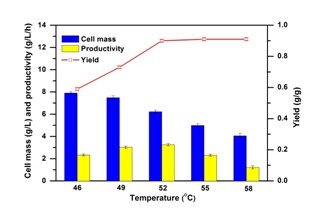
(b) Effects of temperature on lactic acid production; (Image by IPE)
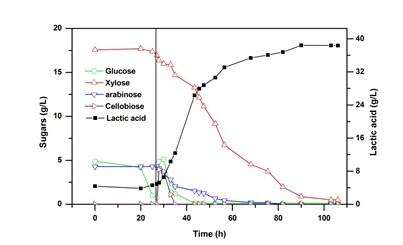
(c) Profile of SSCF with wheat straw by B. coagulans IPE22. (Image by IPE)
Lactic acid is an important chemical with versatile applications in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries. Recent demands for lactic acid have surged due to the increasing manufacture of environment-friendly poly lactic acid. During the production of lactic acid by fermentation, the cost of the carbon source is very significant. Hence, lignocellulosic materials are regarded as suitable feedstocks for lactic acid production. However, due to the limitation of strain, the process of lactic acid production from lignocellulose is usually divided into individual operating units, including biomass pretreatment, hemicellulosic hydrolysates detoxification and fermentation, cellulose saccharification and fermentation. The separated operations make the overall process inefficient and thus the commercial production of lactic acid from lignocellulose is uneconomical.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. WAN Yinhua at Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences isolated a thermophilic lactic acid producer, Bacillus coagulans strain IPE22. With this strain, an efficient process was also developed for lactic acid production from wheat straw.
B. coagulans IPE22 showed remarkable capability to ferment pentose, hexose and cellobiose at temperature above 50°C, and was also resistant to inhibitors from lignocellulosic hydrolysates. Based on the strain’s promising features, an efficient process was developed to produce lactic acid from wheat straw. The process consisted of biomass pretreatment by dilute sulfuric acid and subsequent SSCF (simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation). The operations of solid-liquid separation and detoxification were avoided, and the slurry of pretreated wheat straw was directly fermented. Using this process, 46.12 g lactic acid could be produced from 100 g dry wheat straw with 20 FPU (filter paper activity units)/g cellulose and 10 g/L corn steep liquid powder as nitrogen source. The process by B. coagulans IPE22 provides an economical route to produce lactic acid from lignocellulose.
This work has been published in Bioresource Technology, 2014, 158: 396-399.
 |  |  |
| (a) SEM image of B. coagulans IPE22; (Image by IPE) | (b) Effects of temperature on lactic acid production; (Image by IPE) | (c) Profile of SSCF with wheat straw by B. coagulans IPE22. (Image by IPE) |
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

