
Taking Spatially Confined Reaction to Superlattice Synthesis
Jun 12, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

XIE Yi, professor of materials science and engineering, and her team have developed a new strategy to synthesize superlattice, which is based on spatially confined reaction.Superlattice has fascinating properties which open new opportunities to design new materials. However, the main drawback of superlattice lies in its synthesis and traditional methods like pulsed laser deposition or molecular beam epitaxy, which require complex and expensive process from the growth substrate for final application. Based on recent progress in graphene, XIE Yi and her collaborators introduce spatially confined reaction to superlattice synthesis.They find 2-D graphene layers can not only provide confined reacting space, but also act as electron donor to reduce formation energy in their reacting system. To prove their hypothesis, XIE’s group experimentally obtains the perfect freestanding and flexible vanadium oxide/graphene superlattice nanosheets via this method. Moreover, they observe enhanced magnetocaloric effect and smart switching behavior in electrical conductivity. It can be predicted that this new finding will be quite meaningful when applied to intelligent devices.This work has been published in Nature Communications on June 3, entitled "Magnetocaloric effects in a freestanding and flexible graphene-based superlattice synthesized with a spatially confined reaction".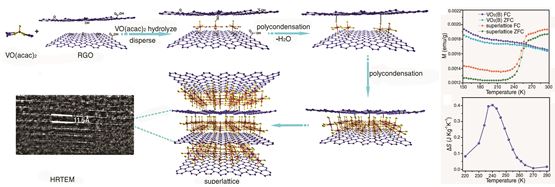
Schematic representation of the formation mechanism for the superlattice through space-confined nanoreactor strategy (Image by XIE Yi's team)
XIE Yi, professor of materials science and engineering, and her team have developed a new strategy to synthesize superlattice, which is based on spatially confined reaction.
Superlattice has fascinating properties which open new opportunities to design new materials. However, the main drawback of superlattice lies in its synthesis and traditional methods like pulsed laser deposition or molecular beam epitaxy, which require complex and expensive process from the growth substrate for final application. Based on recent progress in graphene, XIE Yi and her collaborators introduce spatially confined reaction to superlattice synthesis.
They find 2-D graphene layers can not only provide confined reacting space, but also act as electron donor to reduce formation energy in their reacting system. To prove their hypothesis, XIE’s group experimentally obtains the perfect freestanding and flexible vanadium oxide/graphene superlattice nanosheets via this method. Moreover, they observe enhanced magnetocaloric effect and smart switching behavior in electrical conductivity. It can be predicted that this new finding will be quite meaningful when applied to intelligent devices.
This work has been published in Nature Communications on June 3, entitled "Magnetocaloric effects in a freestanding and flexible graphene-based superlattice synthesized with a spatially confined reaction".

Schematic representation of the formation mechanism for the superlattice through space-confined nanoreactor strategy (Image by XIE Yi's team)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

