
Scientists Reveal Molecular Mechanism of Lis1 in Regulating Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Fetal Liver
Jun 11, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

In order to sustain lifelong hematopoiesis, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) undergo an expansion in the fetal liver to establish a functional HSC pool during their development. The mechanism that regulates fetal liver HSC (FL-HSC) expansion is largely unknown. Though many growth factors such as insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) and stem cell factor (SCF) have been shown to regulate the proliferation and maintenance of FL-HSCs, the intrinsic factors that directly regulate FL-HSC expansion remain to be investigated.
Under the supervision of Prof. LIU Xiaolong at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology (SIBCB), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, CHEN Xufeng, ZHANG Jiali and their colleagues have revealed a critical role of Lis1 in regulating the expansion of FL-HSCs.
Briefly, in the absent of Lis1, FL-HSCs form multipolar mitotic spindles after several rounds of division. As a result, they fail to properly segregate their chromosomes and become anenploid, which will finally trigger apoptosis and rapid cell death in a cell division dependent manner. Owing to the property that FL-HSCs are continuously dividing during their expansion, such a serious survival defect eventually leads to a total failure in the expansion of FL-HSCs and embryonic lethality. Altogether, this study identifies Lis1 as a key regulator that sustains FL-HSC expansion.
The paper entitled "Lis1 is required for the expansion of hematopoietic stem cells in the fetal liver" was published online in Cell Research on May 23th, 2014. The work was done in collaboration with Prof. ZHAO Mujun at SIBCB, and supported by grants from 973 program and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
CONTACT:
LIU Xiaolong, Principle Investigator
Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences|
Shanghai 200031, China.
Email: liux@sibs.ac.cn
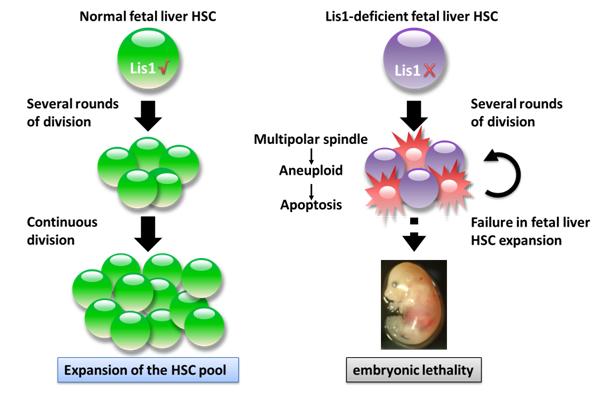
The critical function of Lis1 in regulating the expansion of FL-HSCs. (Image by Prof. LIU Xiaolong’s group)
In order to sustain lifelong hematopoiesis, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) undergo an expansion in the fetal liver to establish a functional HSC pool during their development. The mechanism that regulates fetal liver HSC (FL-HSC) expansion is largely unknown. Though many growth factors such as insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) and stem cell factor (SCF) have been shown to regulate the proliferation and maintenance of FL-HSCs, the intrinsic factors that directly regulate FL-HSC expansion remain to be investigated.
Under the supervision of Prof. LIU Xiaolong at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology (SIBCB), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, CHEN Xufeng, ZHANG Jiali and their colleagues have revealed a critical role of Lis1 in regulating the expansion of FL-HSCs.
Briefly, in the absent of Lis1, FL-HSCs form multipolar mitotic spindles after several rounds of division. As a result, they fail to properly segregate their chromosomes and become anenploid, which will finally trigger apoptosis and rapid cell death in a cell division dependent manner. Owing to the property that FL-HSCs are continuously dividing during their expansion, such a serious survival defect eventually leads to a total failure in the expansion of FL-HSCs and embryonic lethality. Altogether, this study identifies Lis1 as a key regulator that sustains FL-HSC expansion.
The paper entitled "Lis1 is required for the expansion of hematopoietic stem cells in the fetal liver" was published online in Cell Research on May 23th, 2014. The work was done in collaboration with Prof. ZHAO Mujun at SIBCB, and supported by grants from 973 program and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
CONTACT:
LIU Xiaolong, Principle Investigator
Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences|
Shanghai 200031, China.
Email: liux@sibs.ac.cn

The critical function of Lis1 in regulating the expansion of FL-HSCs. (Image by Prof. LIU Xiaolong’s group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

