
New Study Reveals Mechanism for HBV Viral mRNA Export
May 08, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

To maximize the production of viral proteins, several viruses, including Hepatitis B virus (HBV), have evolved proteins and/or cis-acting RNA elements that specifically recruit cellular mRNA export factors for exporting viral mRNAs. HBV encodes several intronless viral mRNAs. Expression of viral intronless mRNAs that encode surface proteins is dependent upon a cis-element named post-transcriptional regulatory element (PRE). However, the nuclear export pathway that is used by PRE remains unclear.
A research team led by Prof. CHENG Hong at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. LI Guohui at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, revealed the mechanism for PRE-mediated nuclear export of intronless mRNAs.
By systematic deletion analysis, they identified a 116-nt functional Sub-Element of PRE (SEP1). The RNP forming on the SEP1 RNA was affinity purified, in which the mRNA export machinery TREX as well as several other proteins were identified. They further found that TREX and the SEP1-associating protein ZC3H18 are required for SEP1-mediated mRNA export. They demonstrated that SEP1 directly binds ZC3H18, which recruits TREX to promote nuclear export of intronless mRNAs. This work not only demonstrated the export pathway utilized by HBV PRE, but also provided potential drug targets for anti-HBV strategies.
By studying the cellular binding partners of SEP1-RNA, the researches also identified several novel cellular mRNA export factors, which might function in recruiting the export machinery TREX to cellular mRNAs. This result provided important insights into the mechanistic study of cellular mRNA export.
This study entitled “A Sub-Element in PRE enhances nuclear export of intronless mRNAs by recruiting the TREX complex via ZC3H18” was published online in Nucleic Acids Research on Apr. 29, 2014. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
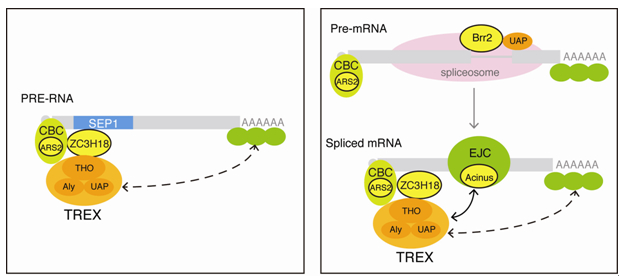
Models for the roles of SEP1-associating proteins in the nuclear export of PRE-containing mRNAs and spliced cellular mRNAs. (Image by Prof. CHENG Hong’s group)
To maximize the production of viral proteins, several viruses, including Hepatitis B virus (HBV), have evolved proteins and/or cis-acting RNA elements that specifically recruit cellular mRNA export factors for exporting viral mRNAs. HBV encodes several intronless viral mRNAs. Expression of viral intronless mRNAs that encode surface proteins is dependent upon a cis-element named post-transcriptional regulatory element (PRE). However, the nuclear export pathway that is used by PRE remains unclear.
A research team led by Prof. CHENG Hong at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. LI Guohui at the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, revealed the mechanism for PRE-mediated nuclear export of intronless mRNAs.
By systematic deletion analysis, they identified a 116-nt functional Sub-Element of PRE (SEP1). The RNP forming on the SEP1 RNA was affinity purified, in which the mRNA export machinery TREX as well as several other proteins were identified. They further found that TREX and the SEP1-associating protein ZC3H18 are required for SEP1-mediated mRNA export. They demonstrated that SEP1 directly binds ZC3H18, which recruits TREX to promote nuclear export of intronless mRNAs. This work not only demonstrated the export pathway utilized by HBV PRE, but also provided potential drug targets for anti-HBV strategies.
By studying the cellular binding partners of SEP1-RNA, the researches also identified several novel cellular mRNA export factors, which might function in recruiting the export machinery TREX to cellular mRNAs. This result provided important insights into the mechanistic study of cellular mRNA export.
This study entitled “A Sub-Element in PRE enhances nuclear export of intronless mRNAs by recruiting the TREX complex via ZC3H18” was published online in Nucleic Acids Research on Apr. 29, 2014. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.

Models for the roles of SEP1-associating proteins in the nuclear export of PRE-containing mRNAs and spliced cellular mRNAs. (Image by Prof. CHENG Hong’s group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

