
Polycarboxybetaine Modified Cationic Liposomes Enhancing SIRNA Therapeutic Efficiency for Hypercholesterolemia Regression
May 15, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Cationic liposomes hold great promising application for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia-related diseases owing to their ability to improve the in vitro and in vivo activity of the encapsulated drug. However, cationic liposomes have nonspecific interaction with plasma protein in vivo and are prone to be rapidly cleared from the circulatory system. Although modification of cationic liposomes with polyethylene glycol (PEG) could prolong the circulation lifetime, PEG significantly inhibits endosomal/lysosomal escape of liposomes, resulting in low therapeutic efficiency. Therefore, it is urgently needed to develop a new strategy to extend the circulation time of cationic liposomes without interfering with their therapeutic efficiency.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. ZHANG Xin at the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, explored a new material for cationic liposomes modification to enhance the serum stability and therapeutic efficiency of cationic liposome-based drug delivery system.
The research team synthesized polycarboxybetaine (PCB) based lipid DSPE-PCB with the method of atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). Cationic liposomes with the modification of DSPE-PCB were prepared by thin lipid film method. The PCBylated cationic liposomes showed excellent stability in serum medium. The siRNA encapsulation efficiency of DSPE-PCB lipoplexes could reach 92% at N/P ratio of 20/1, while only 73% for DSPE-PEG lipoplexes. The pH-sensibility of DSPE-PCB lipoplexes promoted the endosomal/lysosomal escape capacity of cationic liposome/siRNA lipoplexes as detected by IN Cell Analyzer 2000. In vivo functional studies of liver section observed under confocal microscopy indicated that siRNA could be successfully delivered to liver by DSPE-PCB cationic liposomes. DSPE-PCB lipoplexes treated livers showed an inhibition of 62% of ApoB mRNA expression and consequently decrease the total cholesterol in serum in vivo. With excellent in vivo therapeutic efficiency, DSPE-PCB has the potential to alternative commercial DSPE-PEG lipid to modify cationic liposomes for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia-related disease.
The results have been published on Journal of Controlled Release, 2014, 176: 104-114.
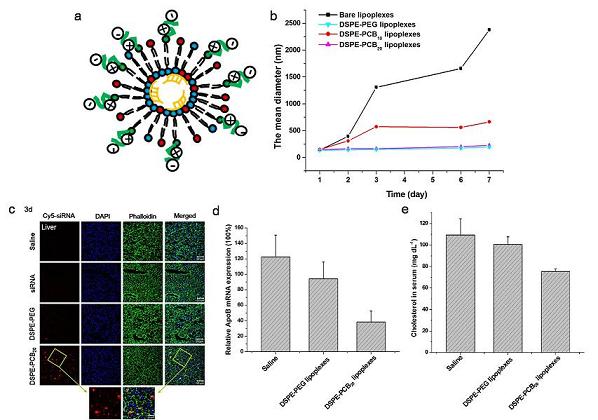
Figure a) Schematic diagram of DSPE-PCB cationic liposome-siRNA lipoplexes. b) Changes in particle diameters of the lipoplexes at N/P ratio of 10/1 following incubation with DMEM containing 10% FBS. c) Liver section observed under confocal microscopy. d) Relative ApoB mRNA expression occurred in livers suffered lipoplexes treatment. e) The measurement of total CHO in serum. (Image by IPE)
Cationic liposomes hold great promising application for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia-related diseases owing to their ability to improve the in vitro and in vivo activity of the encapsulated drug. However, cationic liposomes have nonspecific interaction with plasma protein in vivo and are prone to be rapidly cleared from the circulatory system. Although modification of cationic liposomes with polyethylene glycol (PEG) could prolong the circulation lifetime, PEG significantly inhibits endosomal/lysosomal escape of liposomes, resulting in low therapeutic efficiency. Therefore, it is urgently needed to develop a new strategy to extend the circulation time of cationic liposomes without interfering with their therapeutic efficiency.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. ZHANG Xin at the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, explored a new material for cationic liposomes modification to enhance the serum stability and therapeutic efficiency of cationic liposome-based drug delivery system.
The research team synthesized polycarboxybetaine (PCB) based lipid DSPE-PCB with the method of atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP). Cationic liposomes with the modification of DSPE-PCB were prepared by thin lipid film method. The PCBylated cationic liposomes showed excellent stability in serum medium. The siRNA encapsulation efficiency of DSPE-PCB lipoplexes could reach 92% at N/P ratio of 20/1, while only 73% for DSPE-PEG lipoplexes. The pH-sensibility of DSPE-PCB lipoplexes promoted the endosomal/lysosomal escape capacity of cationic liposome/siRNA lipoplexes as detected by IN Cell Analyzer 2000. In vivo functional studies of liver section observed under confocal microscopy indicated that siRNA could be successfully delivered to liver by DSPE-PCB cationic liposomes. DSPE-PCB lipoplexes treated livers showed an inhibition of 62% of ApoB mRNA expression and consequently decrease the total cholesterol in serum in vivo. With excellent in vivo therapeutic efficiency, DSPE-PCB has the potential to alternative commercial DSPE-PEG lipid to modify cationic liposomes for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia-related disease.
The results have been published on Journal of Controlled Release, 2014, 176: 104-114.

Figure a) Schematic diagram of DSPE-PCB cationic liposome-siRNA lipoplexes. b) Changes in particle diameters of the lipoplexes at N/P ratio of 10/1 following incubation with DMEM containing 10% FBS. c) Liver section observed under confocal microscopy. d) Relative ApoB mRNA expression occurred in livers suffered lipoplexes treatment. e) The measurement of total CHO in serum. (Image by IPE)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

