
Spark Plasma Sintering of New High Temperature NTC Thermistor Ceramics Based on MgAl2O4-YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 Composite System
May 04, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors are widely used in various industrial and domestic applications. However, the popular NTC materials based on spinel forming oxide systems are commonly limited to temperatures below 300°C as a result of the instability and changing electrical characteristics. Therefore, there is a need to develop new materials that have good electrical characteristics at high temperatures.
Professor CHANG Aimin’s group from Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry (XTIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, designed and prepared xMgAl2O4-(1-x)YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 high temperature composite thermistor ceramics by associating a less resistive phase YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 with a high resistive MgAl2O4 combination with spark plasma sintering (SPS). The structure, microstructure and electrical properties of composite ceramics have also been investigated. The SPS-sintere composite ceramics consist of a cubic spinel MgAl2O4 phase and an orthorhombic perovskite YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 phase isomorphic to YCrO3. The relative densities of SPS-sintered composite ceramics are 95.5%,97.4% and 94.1% of the theoretical density for x=0.1,0.4,0.6, respectively. The resistivity of composite ceramics decreases with increasing temperature from 25 to 1000 ◦C, indicative of NTC characteristics. The obtained ρ25, B25-150, B700-1000, Ea25/150 and Ea700/1000 of the SPS-sintered composite NTC thermistors were in the range of 1.53×106-9.92×109 Ωcm, 3380-5172 K, 7239-9543 K, 0.291~0.446 eV,0.624~0.823 eV, respectively. The proposed method will provide theoretical foundation for designing new high temperature NTC thermistor materials.
The research results have been published in Journal of the European Ceramic Society. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China.
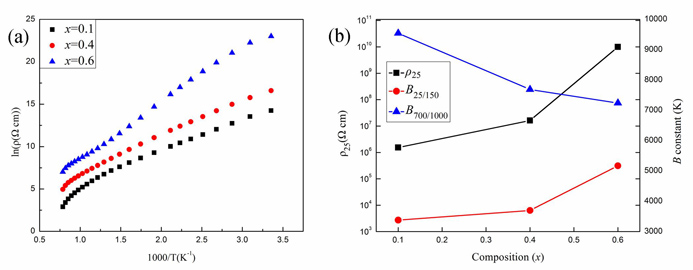
Fig.1. (a) Relationship between lnρ and 1000/T for the SPS-sintered samples. (b) Evolution of ρ25 and B constants as a function of MgAl2O4 content (x) for the SPS-sintered samples. (Image by XTIPC)
Negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors are widely used in various industrial and domestic applications. However, the popular NTC materials based on spinel forming oxide systems are commonly limited to temperatures below 300°C as a result of the instability and changing electrical characteristics. Therefore, there is a need to develop new materials that have good electrical characteristics at high temperatures.
Professor CHANG Aimin’s group from Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry (XTIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, designed and prepared xMgAl2O4-(1-x)YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 high temperature composite thermistor ceramics by associating a less resistive phase YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 with a high resistive MgAl2O4 combination with spark plasma sintering (SPS). The structure, microstructure and electrical properties of composite ceramics have also been investigated. The SPS-sintere composite ceramics consist of a cubic spinel MgAl2O4 phase and an orthorhombic perovskite YCr0.5Mn0.5O3 phase isomorphic to YCrO3. The relative densities of SPS-sintered composite ceramics are 95.5%,97.4% and 94.1% of the theoretical density for x=0.1,0.4,0.6, respectively. The resistivity of composite ceramics decreases with increasing temperature from 25 to 1000 ◦C, indicative of NTC characteristics. The obtained ρ25, B25-150, B700-1000, Ea25/150 and Ea700/1000 of the SPS-sintered composite NTC thermistors were in the range of 1.53×106-9.92×109 Ωcm, 3380-5172 K, 7239-9543 K, 0.291~0.446 eV,0.624~0.823 eV, respectively. The proposed method will provide theoretical foundation for designing new high temperature NTC thermistor materials.
The research results have been published in Journal of the European Ceramic Society. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China.

Fig.1. (a) Relationship between lnρ and 1000/T for the SPS-sintered samples. (b) Evolution of ρ25 and B constants as a function of MgAl2O4 content (x) for the SPS-sintered samples. (Image by XTIPC)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

