
Research of OCPs in Surface Sediments from the East Lake Promotes Strategic Environmental Management
May 09, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) are ubiquitous pollutants and their presence in urban lakes is a concern for human and ecological health. OCPs can be introduced into the aquatic environment by discharge of domestic sewage and industrial wastewater, runoff from non-point sources, agriculture inputs, wet or dry deposition and other means. Due to their low water solubility and high octanol-water partition coefficient (KOW) values, OCPs tend to accumulate in sediments. Sediments, one of the important sources and sinks of OCPs, can be resuspended and released bound-OCPs from particles into water under certain conditions, which can result in secondary contamination of water.
The East Lake, located in Wuhan, is the largest urban lake in China. The lake is very important for fishery production and life of local residents and tourists for water supply, aquatic sport, and recreation. However, with the rapid industrialization and urbanization, environmental pollution around the lake has been constantly increasing during the past three decades.
Master candidate YUN Xiaoyan under the supervision of Professor WANG Jun from Key Laboratory of Aquatic Botany and Watershed Ecology, Wuhan Botanical Garden evaluated the concentrations, distributions, sources and risk assessment of OCPs in surface sediments from the East Lake, China.
The total concentrations of 14 OCPs ranged from 6.3 to 400 ng g-1 dry weight (dw) with an average concentration of 79 ng g-1 dw. The mean values of HCHs and DDTs were 36 and 7.6 ng g-1 dw, accounting for 45% and 10% of the total OCPs, respectively. Composition analyses indicated that DDTs and endosulfan were mainly from historical contribution. Historical use of technical HCH and new input of lindane were probably the source of HCHs in the East Lake.
Results were published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research entitled “Distribution and ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments from the East Lake, China”. This project was supported in part by Open Funding Project of the Key Laboratory of Aquatic Botany and Watershed Ecology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Open Funding Project of The State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science, Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China, and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
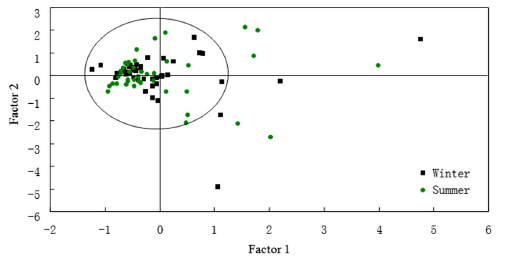
Loading plot of factor analysis based on concentration of OCPs in the East Lake, China (Image by WBG)
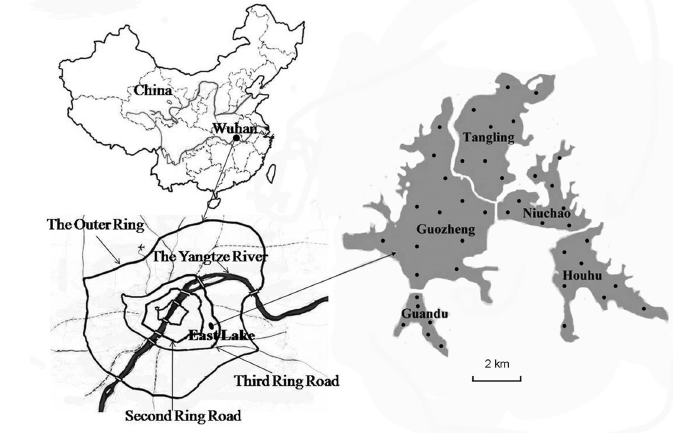
Locations of study area in the East Lake, China (Image by WBG)
Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) are ubiquitous pollutants and their presence in urban lakes is a concern for human and ecological health. OCPs can be introduced into the aquatic environment by discharge of domestic sewage and industrial wastewater, runoff from non-point sources, agriculture inputs, wet or dry deposition and other means. Due to their low water solubility and high octanol-water partition coefficient (KOW) values, OCPs tend to accumulate in sediments. Sediments, one of the important sources and sinks of OCPs, can be resuspended and released bound-OCPs from particles into water under certain conditions, which can result in secondary contamination of water.
The East Lake, located in Wuhan, is the largest urban lake in China. The lake is very important for fishery production and life of local residents and tourists for water supply, aquatic sport, and recreation. However, with the rapid industrialization and urbanization, environmental pollution around the lake has been constantly increasing during the past three decades.
Master candidate YUN Xiaoyan under the supervision of Professor WANG Jun from Key Laboratory of Aquatic Botany and Watershed Ecology, Wuhan Botanical Garden evaluated the concentrations, distributions, sources and risk assessment of OCPs in surface sediments from the East Lake, China.
The total concentrations of 14 OCPs ranged from 6.3 to 400 ng g-1 dry weight (dw) with an average concentration of 79 ng g-1 dw. The mean values of HCHs and DDTs were 36 and 7.6 ng g-1 dw, accounting for 45% and 10% of the total OCPs, respectively. Composition analyses indicated that DDTs and endosulfan were mainly from historical contribution. Historical use of technical HCH and new input of lindane were probably the source of HCHs in the East Lake.
Results were published in Environmental Science and Pollution Research entitled “Distribution and ecological risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments from the East Lake, China”. This project was supported in part by Open Funding Project of the Key Laboratory of Aquatic Botany and Watershed Ecology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Open Funding Project of The State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science, Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China, and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.

Loading plot of factor analysis based on concentration of OCPs in the East Lake, China (Image by WBG)

Locations of study area in the East Lake, China (Image by WBG)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

