
Evaluation of PCBs and PBDEs Ecotoxicological Risk Enlightens TGD Proctection
Apr 30, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are halogenated compounds originating from anthropogenic sources. These compounds have become ubiquitous in environmental and biological samples worldwide due to their persistence and long-range transport, which causes negative health effects.
Dr. GE Jing, under the supervision of Prof. WANG Jun from Wuhan Botanical Garden investigated the distributions, potential sources and ecotoxicological risks of 32 PCBs and 10 PBDEs in the surface water of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) region (Yangtze River, China). Samples collected from 18 sites of theupstream (UTGD) and downstream (DTGD) of the TGD were analyzed.
Independent-samples t test showed no statistical significance of ∑PCBs and ∑PBDEs between the UTGD and DTGD samples. However, linear regression analysis indicated a declining trend of both ∑PCBs and ∑PBDEs from the UTGD to DTGD and site 11 got relatively higher concentrations of both PCBs and PBDEs, indicating that materials accumulated behind the dam have become a source of PCBs and PBDEs in the Yangtze River. Principal component analysis indicated the difference of potential sources of PCBs and PBDEs in the study area. The potential eco-toxicological risk of PCBs in surface water of the TGD region is very low, whereas special attention needs to be paid to PBDEs in the study area.
This research was funded by the “Hundred Talents Program”, and the Knowledge Innovative Key Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Results were published in Ecotoxicology entitled “Distribution, potential source and ecotoxicological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the surface water of the Three Gorges Dam region of the Yangtze River, China”.
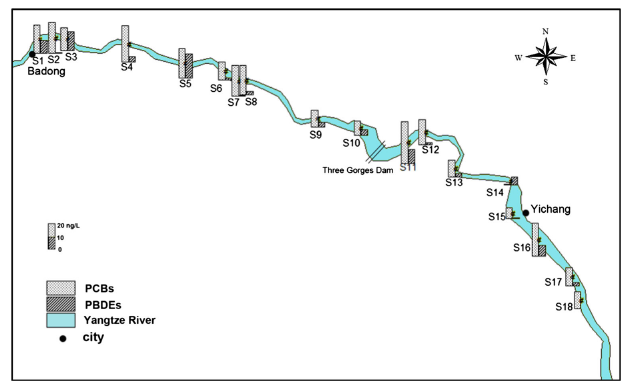
Distribution of total PCBs and PBDEs at 18 sampling sites of the ThreeGorges Dam region of the Yangtze River (Image by WBG)
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are halogenated compounds originating from anthropogenic sources. These compounds have become ubiquitous in environmental and biological samples worldwide due to their persistence and long-range transport, which causes negative health effects.
Dr. GE Jing, under the supervision of Prof. WANG Jun from Wuhan Botanical Garden investigated the distributions, potential sources and ecotoxicological risks of 32 PCBs and 10 PBDEs in the surface water of the Three Gorges Dam (TGD) region (Yangtze River, China). Samples collected from 18 sites of theupstream (UTGD) and downstream (DTGD) of the TGD were analyzed.
Independent-samples t test showed no statistical significance of ∑PCBs and ∑PBDEs between the UTGD and DTGD samples. However, linear regression analysis indicated a declining trend of both ∑PCBs and ∑PBDEs from the UTGD to DTGD and site 11 got relatively higher concentrations of both PCBs and PBDEs, indicating that materials accumulated behind the dam have become a source of PCBs and PBDEs in the Yangtze River. Principal component analysis indicated the difference of potential sources of PCBs and PBDEs in the study area. The potential eco-toxicological risk of PCBs in surface water of the TGD region is very low, whereas special attention needs to be paid to PBDEs in the study area.
This research was funded by the “Hundred Talents Program”, and the Knowledge Innovative Key Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Results were published in Ecotoxicology entitled “Distribution, potential source and ecotoxicological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the surface water of the Three Gorges Dam region of the Yangtze River, China”.

Distribution of total PCBs and PBDEs at 18 sampling sites of the ThreeGorges Dam region of the Yangtze River (Image by WBG)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

