
New Study Reveals QKI as Critical Regulator of Aberrant Splicing in Lung Cancer
Apr 23, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Alternative pre-mRNA splicing is a key mechanism for increasing proteomic diversity and modulating gene expression. Emerging evidence indicates that splicing program is frequently deregulated during tumorigenesis. Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Although a number of lung cancer-related splicing events have been detected in several genome-wide analyses, much less is known about how aberrant splicing takes place in lung cancer and how it contributes to tumor development.
Under the supervision of Prof. HUI Jingyi at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, graduate student ZONG Fengyang, Dr. FU Xing, and colleagues identified the RNA-binding protein QKI as a new critical regulator of alternative splicing in lung cancer and as a potential early marker for prognosis. They demonstrated that QKI inhibits the proliferation and transformation of lung cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. They provided evidence that QKI regulates the alternative splicing of NUMB via competing with a core splicing factor SF1, thereby suppressing cell proliferation and preventing the activation of the Notch signaling pathway.
This work characterized the RNA-binding protein QKI as a new critical regulator of alternative splicing, suggesting a novel tumor suppression pathway, and expanding the understanding of splicing regulation in tumorigenesis.
This study entitled “The RNA-Binding Protein QKI Suppresses Cancer-Associated Aberrant Splicing” was published online in PLOS Genetics on April 10, 2014. This work was done in collaboration with Prof. JI Hongbin, and supported by grants from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Basic Research Program of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
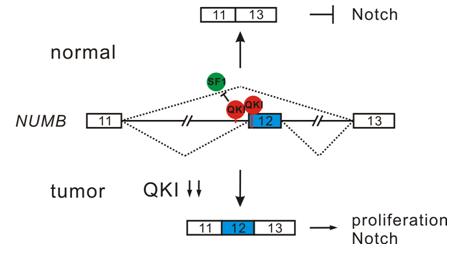
A scheme showing a new tumor suppression pathway involving QKI-mediated regulation of the Notch signaling pathway. (Image by Prof. HUI Jingyi’s group)
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing is a key mechanism for increasing proteomic diversity and modulating gene expression. Emerging evidence indicates that splicing program is frequently deregulated during tumorigenesis. Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Although a number of lung cancer-related splicing events have been detected in several genome-wide analyses, much less is known about how aberrant splicing takes place in lung cancer and how it contributes to tumor development.
Under the supervision of Prof. HUI Jingyi at the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, graduate student ZONG Fengyang, Dr. FU Xing, and colleagues identified the RNA-binding protein QKI as a new critical regulator of alternative splicing in lung cancer and as a potential early marker for prognosis. They demonstrated that QKI inhibits the proliferation and transformation of lung cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. They provided evidence that QKI regulates the alternative splicing of NUMB via competing with a core splicing factor SF1, thereby suppressing cell proliferation and preventing the activation of the Notch signaling pathway.
This work characterized the RNA-binding protein QKI as a new critical regulator of alternative splicing, suggesting a novel tumor suppression pathway, and expanding the understanding of splicing regulation in tumorigenesis.
This study entitled “The RNA-Binding Protein QKI Suppresses Cancer-Associated Aberrant Splicing” was published online in PLOS Genetics on April 10, 2014. This work was done in collaboration with Prof. JI Hongbin, and supported by grants from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Basic Research Program of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.

A scheme showing a new tumor suppression pathway involving QKI-mediated regulation of the Notch signaling pathway. (Image by Prof. HUI Jingyi’s group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

