
New study Reveals Novel Molecular Mechanisms of Plant Thermotolerance
Apr 14, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Heat stress causes extensive losses in agricultural production worldwide. Plants subjected to heat stress have evolved a variety of mechanisms to respond to high temperatures that minimize damage and ensure protection of cellular homeostasis. Central to the heat stress response in plants are the heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and heat stress proteins (Hsps). However, the understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms of thermotolerance is limited.
Researchers from Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted a study in HTT1 mediates plant thermotolerance.
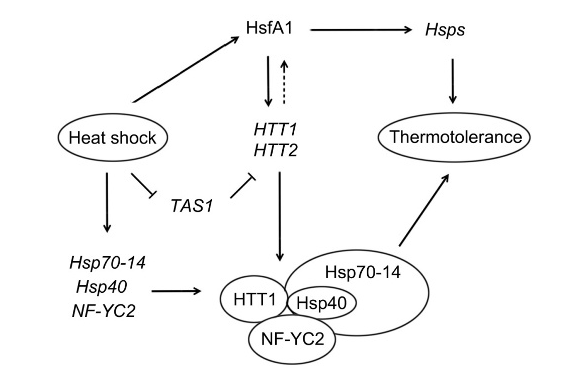
Dr. HE Yuke and his team in Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences identified a role of unknown protein HTT1 in thermotolerance. Overexpression of TAS1a, whose trans-acting small interfering RNAs target the HTT genes, elevated accumulation of TAS1-siRNAs and reduced expression levels of the HTT genes, causing weaker thermotolerance. By contrast, overexpression of HTT1 upregulated several Hsf genes, and lead to stronger thermotolerance. Meanwhile, HsfA1a directly activated HTT genes through binding to their promoters. Further analysis revealed that HTT1 interacted with Hsp70-14, Hsp40, and NUCLEAR FACTOR Y, SUBUNIT C2, acting as cofactor of Hsp70-14 complexes. This research brings a new insight into understanding the mechanism of the plant heat stress response network.
This work entitled “HEAT-INDUCED TAS1 TARGET1 Mediates Thermotolerance via HEAT STRESS TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR A1a–Directed Pathways in Arabidopsis” was published in The Plant Cell on April, 2014. This research was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (Grant 2012CB113903).
Heat stress causes extensive losses in agricultural production worldwide. Plants subjected to heat stress have evolved a variety of mechanisms to respond to high temperatures that minimize damage and ensure protection of cellular homeostasis. Central to the heat stress response in plants are the heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and heat stress proteins (Hsps). However, the understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms of thermotolerance is limited.
Researchers from Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted a study in HTT1 mediates plant thermotolerance.
Dr. HE Yuke and his team in Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences identified a role of unknown protein HTT1 in thermotolerance. Overexpression of TAS1a, whose trans-acting small interfering RNAs target the HTT genes, elevated accumulation of TAS1-siRNAs and reduced expression levels of the HTT genes, causing weaker thermotolerance. By contrast, overexpression of HTT1 upregulated several Hsf genes, and lead to stronger thermotolerance. Meanwhile, HsfA1a directly activated HTT genes through binding to their promoters. Further analysis revealed that HTT1 interacted with Hsp70-14, Hsp40, and NUCLEAR FACTOR Y, SUBUNIT C2, acting as cofactor of Hsp70-14 complexes. This research brings a new insight into understanding the mechanism of the plant heat stress response network.
This work entitled “HEAT-INDUCED TAS1 TARGET1 Mediates Thermotolerance via HEAT STRESS TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR A1a–Directed Pathways in Arabidopsis” was published in The Plant Cell on April, 2014. This research was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (Grant 2012CB113903).

CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

