
New Cathode Material of Li-ion Batteries Developed
Apr 15, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Discovering the electrode materials with high energy and power densities is critically important, which enables Li-ion battery technology to meet the requirements of mobile electronic devices and automotive industry. Because of this, layered lithium-rich transition-metal oxides have attracted much attention as one of the most promising cathode materials due to their high reversible capacities and low cost.
However, as promising cathode materials that are required to have high energy and power densities, the inferior rate capability is the major bottleneck of Li-rich layered cathodes. In order to resolve this obstacle, electrochemical kinetics of electrode, including Li+ ion immigration and electron conduction must be further improved.
The research group headed by Prof. LI Liping at Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has designed a solvothermal-precursor method to synthesize spinel-layered Li-rich microspheres, by which a small amount of spinel component is successfully introduced into layered oxides.
Due to the introduction of spinel-like component which has the efficient three-dimensional diffusion of lithium ions, the surface-film and charge-transfer resistances of the spinel-layered Li-rich microsphere electrode material are decreased obviously, and the Li-ion diffusion coefficient of that has significantly increased. All of these are very helpful to improve the rate capability of Li-rich cathode materials.
It is amazing that with the aid of spinel-like component, the discharge capacity of the spinel-layered Li-rich microsphere electrode material is only slightly reduced when the charge-discharge current density increases from 60 to 1200 mA g-1. Results of this study have been published as an article in Adv. Energy Mater. (2014, DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201400062).
Previously, Prof. LI's group had made a series of relevant progress on the new type cathode materials of Li-ion batteries, such as: Li1.2Mn0.4Co0.4O2, Li[Li0.14Mn0.47Ni0.25Co0.14]O2, LiCo0.95Mn0.05O2, LiMn2O4, LiMnPO4, LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and so on. Related research results published in J. Mater. Chem. A (2014, 2, 1471; 2013, 1, 9721; 2013, 1, 1220) and J. Mater. Chem. (2012, 22, 22233).
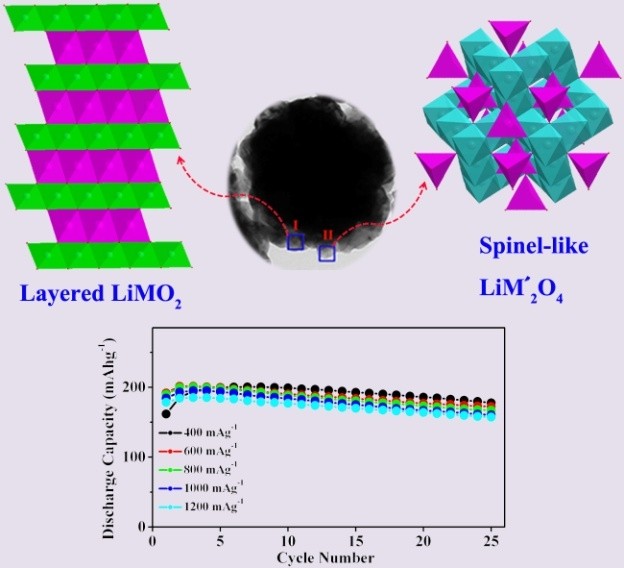
A new spinel-layered lithium-rich microsphere with excellent rate capability was prepared by designing a solvothermal-precursor method. (Image by Prof. LI’s group)
Discovering the electrode materials with high energy and power densities is critically important, which enables Li-ion battery technology to meet the requirements of mobile electronic devices and automotive industry. Because of this, layered lithium-rich transition-metal oxides have attracted much attention as one of the most promising cathode materials due to their high reversible capacities and low cost.
However, as promising cathode materials that are required to have high energy and power densities, the inferior rate capability is the major bottleneck of Li-rich layered cathodes. In order to resolve this obstacle, electrochemical kinetics of electrode, including Li+ ion immigration and electron conduction must be further improved.
The research group headed by Prof. LI Liping at Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has designed a solvothermal-precursor method to synthesize spinel-layered Li-rich microspheres, by which a small amount of spinel component is successfully introduced into layered oxides.
Due to the introduction of spinel-like component which has the efficient three-dimensional diffusion of lithium ions, the surface-film and charge-transfer resistances of the spinel-layered Li-rich microsphere electrode material are decreased obviously, and the Li-ion diffusion coefficient of that has significantly increased. All of these are very helpful to improve the rate capability of Li-rich cathode materials.
It is amazing that with the aid of spinel-like component, the discharge capacity of the spinel-layered Li-rich microsphere electrode material is only slightly reduced when the charge-discharge current density increases from 60 to 1200 mA g-1. Results of this study have been published as an article in Adv. Energy Mater. (2014, DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201400062).
Previously, Prof. LI's group had made a series of relevant progress on the new type cathode materials of Li-ion batteries, such as: Li1.2Mn0.4Co0.4O2, Li[Li0.14Mn0.47Ni0.25Co0.14]O2, LiCo0.95Mn0.05O2, LiMn2O4, LiMnPO4, LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 and so on. Related research results published in J. Mater. Chem. A (2014, 2, 1471; 2013, 1, 9721; 2013, 1, 1220) and J. Mater. Chem. (2012, 22, 22233).

A new spinel-layered lithium-rich microsphere with excellent rate capability was prepared by designing a solvothermal-precursor method. (Image by Prof. LI’s group)
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

