
Context-Aware Service Ranking Serves in Wireless Sensor Networks
Mar 31, 2014 Email"> PrintText Size

Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are widely used in practice for comprehensively monitoring and gathering physical information via a multitude of sensors. As the development of WSNs, the integration of them with the external Internet is urgently needed. By wrapping the sensor functionality as a WSN service, the Web service is considered as the most promising technology to incorporate WSNs into the Internet. The quest for selecting the service with the best performance promotes service ranking technology.
However, because of the dynamic WSN environments, traditional Web service ranking methods that employ user ratings cannot be directly applied to WSN-based services. In this research, in order to fit the characteristics of the WSN environment, a novel context-aware WSN service ranking framework is proposed in Fig.1, which tries to combine both user ratings and WSN services context in the ranking process. The framework consists of four components: service user, service provider, service ranking middleware, and service registry.
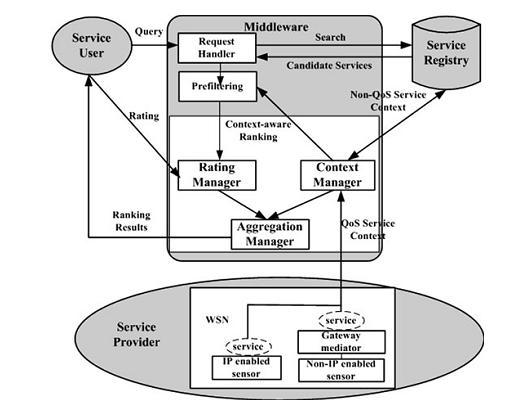
Fig.1 Context-aware WSN service ranking framework (Image by NIU)
The User QoS Assessment (UQA) and Context QoS Assessment (CQA) are proposed, respectively. And then, the variations in the slow convergence user assessment and the quick-variating services’ QoS context factors are further investigated. As well, a Fuzzy aggregation method is put forward to generate a comprehensive assessment for ranking. At last, a case study as a demonstration of the approach’s efficiency is presented.
According to it, in the future, more WSN services for massive experiments will be carried out to verify the applicability of the proposed context-aware WSN service ranking approach. What’s more, the massive data, including users’ ratings and QoS context factor values should also be employed to adjust the fuzzy membership and rules, which brings an interesting direction of the future work.
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61103158, 60903079, 61035003), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Trusted Software, the National S&T Major Project (No. 2010ZX03004-002-01), the Securing CyberSpace Research Lab of Deakin University, the Sino-Finnish International S&T Cooperation and Exchange Program (No. 2010DFB10570), National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB329502) the Strategic Pilot Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDA06010302, XDA06040400), National Science & Technology Pillar Program of China (No. 2012BAH01B03).
The research entitled “Context-Aware Service Ranking in Wireless Sensor Networks” has been published in the Journal of Network and Systems Management (January 2014, Volume 22, Issue 1, pp 50-74).
Contact:
NIU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, People’s Republic of China
E-mail: nwj6688@gmail.com; niuwj@hpnl.ac.cn
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are widely used in practice for comprehensively monitoring and gathering physical information via a multitude of sensors. As the development of WSNs, the integration of them with the external Internet is urgently needed. By wrapping the sensor functionality as a WSN service, the Web service is considered as the most promising technology to incorporate WSNs into the Internet. The quest for selecting the service with the best performance promotes service ranking technology.
However, because of the dynamic WSN environments, traditional Web service ranking methods that employ user ratings cannot be directly applied to WSN-based services. In this research, in order to fit the characteristics of the WSN environment, a novel context-aware WSN service ranking framework is proposed in Fig.1, which tries to combine both user ratings and WSN services context in the ranking process. The framework consists of four components: service user, service provider, service ranking middleware, and service registry.

Fig.1 Context-aware WSN service ranking framework (Image by NIU)
The User QoS Assessment (UQA) and Context QoS Assessment (CQA) are proposed, respectively. And then, the variations in the slow convergence user assessment and the quick-variating services’ QoS context factors are further investigated. As well, a Fuzzy aggregation method is put forward to generate a comprehensive assessment for ranking. At last, a case study as a demonstration of the approach’s efficiency is presented.
According to it, in the future, more WSN services for massive experiments will be carried out to verify the applicability of the proposed context-aware WSN service ranking approach. What’s more, the massive data, including users’ ratings and QoS context factor values should also be employed to adjust the fuzzy membership and rules, which brings an interesting direction of the future work.
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61103158, 60903079, 61035003), Guangxi Key Laboratory of Trusted Software, the National S&T Major Project (No. 2010ZX03004-002-01), the Securing CyberSpace Research Lab of Deakin University, the Sino-Finnish International S&T Cooperation and Exchange Program (No. 2010DFB10570), National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB329502) the Strategic Pilot Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDA06010302, XDA06040400), National Science & Technology Pillar Program of China (No. 2012BAH01B03).
The research entitled “Context-Aware Service Ranking in Wireless Sensor Networks” has been published in the Journal of Network and Systems Management (January 2014, Volume 22, Issue 1, pp 50-74).
Contact:
NIU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, People’s Republic of China
E-mail: nwj6688@gmail.com; niuwj@hpnl.ac.cn
CAS Institutes
There are 124 Institutions directly under the CAS by the end of 2012, with 104 research institutes, five universities & supporting organizations, 12 management organizations that consist of the headquarters and branches, and three other units. Moreover, there are 25 legal entities affiliated and 22 CAS invested holding enterprisesThere are 124 I...>> more
Contact Us

Chinese Academy of Sciences
Add: 52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District, Beijing, China
Postcode: 100864
Tel: 86-10-68597592 (day) 86-10-68597289 (night)
Fax: 86-10-68511095 (day) 86-10-68512458 (night)
E-mail: cas_en@cas.cn

