
Researchers led by Prof. LIN Wenchu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have proposed a mechanism by which circular RNA (circRNA) can promote the progression of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) in vitro and in vivo. Results were published on Molecular Cancer.
Small cell lung cancer was a recalcitrant cancer with limited treatment options. The overall 5-year relative survival rate for SCLC was less than 7%.
Covalently closed circRNAs were single-stranded endogenous RNA molecules with loop structures that played critical roles in cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis, yet the biological functions of circRNAs in SCLC were still elusive.
In this study, the researchers found that circRNA-circVAPA (circular vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein A), which was derived from exons 2-4 of the VAPA gene, exhibited higher expression levels in SCLC than the controls.
"CircVAPA exerts a cancer-promoting effect on SCLC by modulating the miR-377-3p and miR-494-3p/IGF1R/AKT axis," said Prof. LIN, "and this expands our knowledge about circRNAs in SCLC."
Furthermore, circVAPA depletion markedly enhanced the inhibitory effects of BMS-536924, an insulin like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) kinase inhibitor in cellular and xenograft mouse models, providing a novel therapeutic strategy for treating SCLC.
This investigation was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, and a portion of this work was supported by the High Magnetic Field Laboratory of Anhui Province.
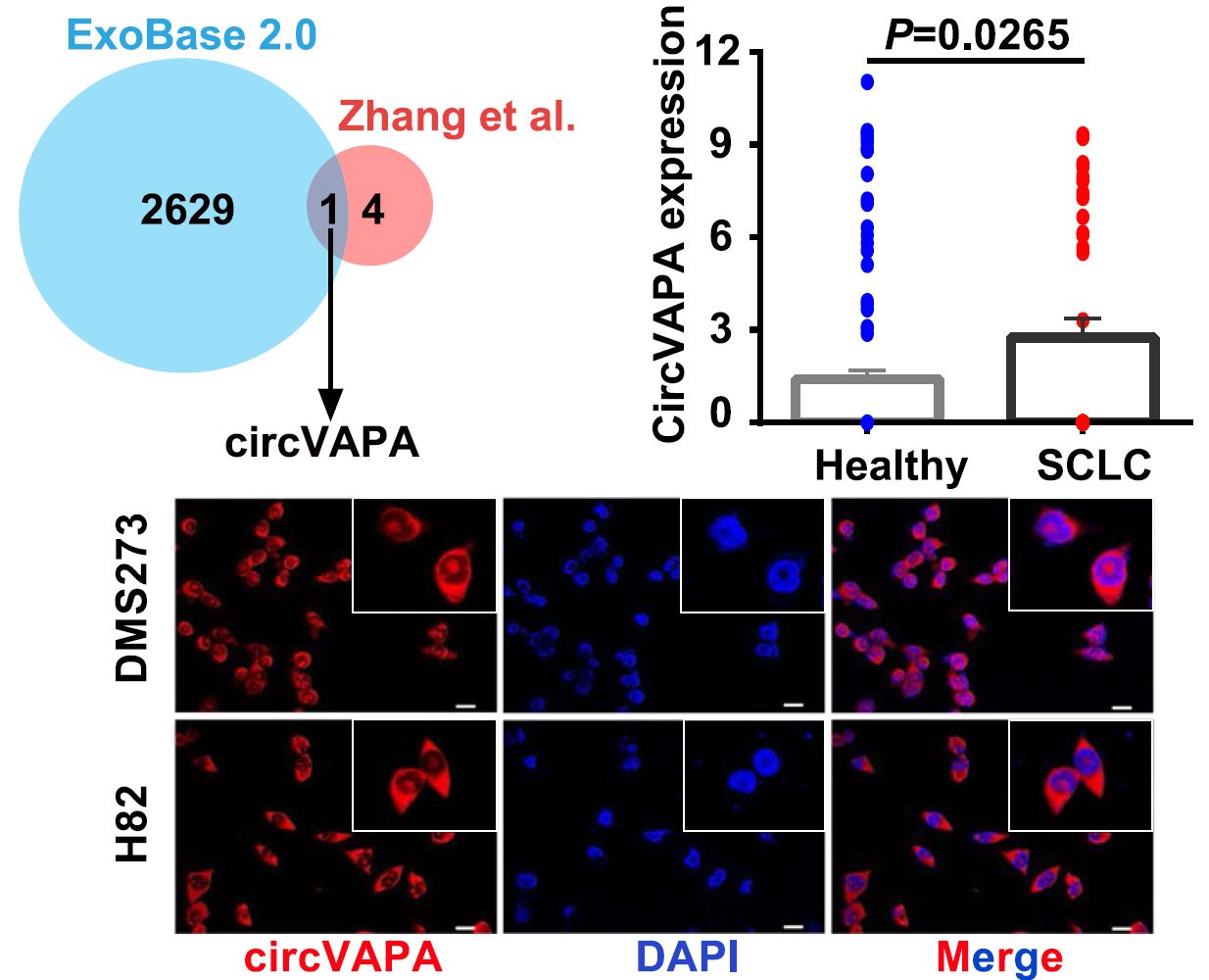
Characterization of circVAPA. (Image by HUA Jinghan)
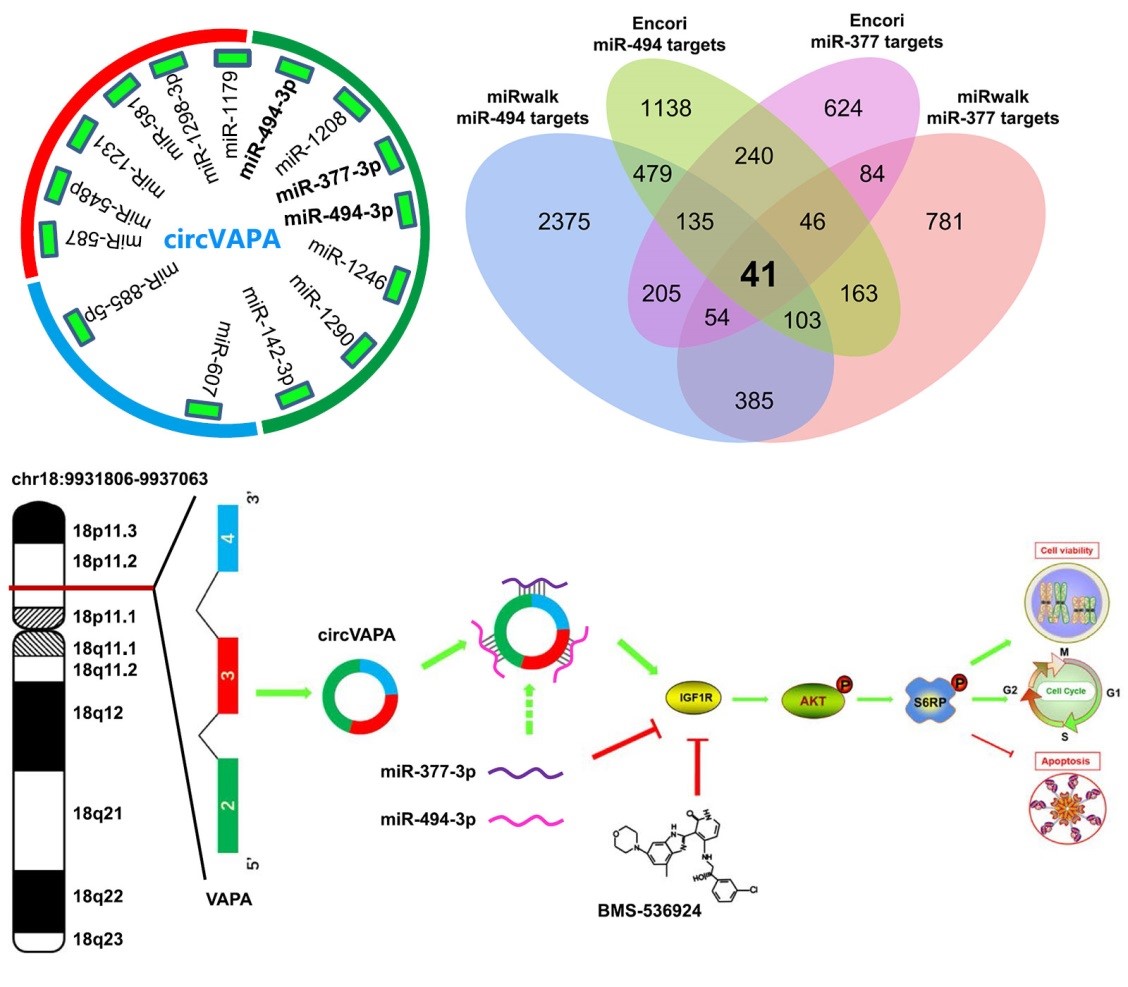
CircVAPA promotes SCLC progression via the miR-377-3p and miR-494-3p/IGF1R/AKT axis. (Image by HUA Jinghan)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

