
According to a recent study published on Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, researchers developed a promising remedy for the rapid and efficient removal of cadmium ion Cd(II) in water, which is a step forward in heavy metal pollution remediation.
Researchers from WU Zhengyan and ZHANG Jia's team at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. CAI Dongqing from Donghua University, have integrated nanoscale zero-valent iron with conductive carbon paint to fabricate a primary battery nanosystem and found the nanocomposite removed Cd(II) in water quickly.
Water contaminated by heavy metal ions has become a worldwide environmental risk for years. Cd(II) is a typical heavy metal ion drawing much concern because of its high toxicity. Developing an economical and environmentally friendly restoration technology remains a huge challenge.
In this study, the researchers revealed the mechanism by studying the interaction between nanocomposites and Cd(II), following an investigation in the removal performance of the nanocomposites under different conditions. Additionally, the biosafety of this strategy was evaluated and the results were proved satisfying.
This study provides a low-cost and environmentally friendly technology for the rapid removal of Cd(II) from water, which has broad application prospects in the environmental field.
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Science and Technology Service Program of CAS and the Key R&D Program of Ningxia Province.
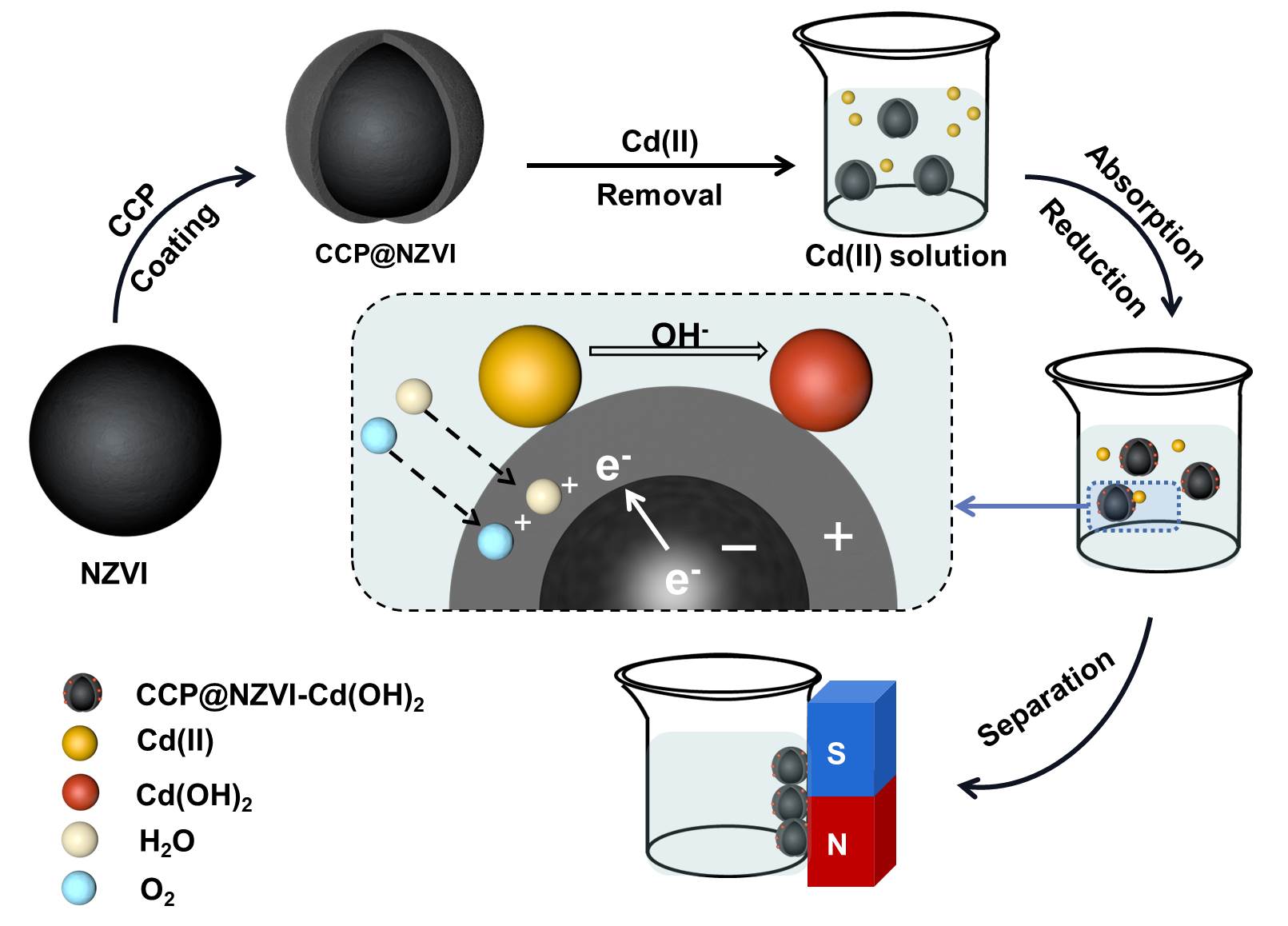
Schematic illustration of removal mechanism. (Image by GUO Xinyue)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

