
The study of stellar activity is associated with many aspects of stellar physics. In the past 40 years, the understanding on stellar activity and its relation with stellar structure and evolution has obtained great progress. One landmark is the discovery of the activity - rotation relation, which indicates the connection between stellar activity and stellar evolution.
However, there are still some fundamental issues to be addressed: why is there a sharp turnoff in the relation and what is the implication of this relation for stars with different dynamos?
Recently, a research team led by Dr. YANG Huiqin at the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) addressed the relation among activity, dynamo, stellar structure and evolution in terms of the flare activity. They proposed a new expression on the activity - rotation relation, which could be an important step in the study of stellar activity.
This study presented a unique method and analysis, which has advantages over the traditional approaches for the study of stellar activity. "The Kepler mission enables us to conduct a systematic study on flares, which could gauge the classical theories from the view of flares. It is important for us to grasp a whole picture and connect various factors for stellar activity," said Prof. LIU Jifeng, coauthor of the study.
They calculated the flare activity of more than 3400 flaring stars for almost all types of stars. They found that the activity - rotation relation in late-type stars was consistent with previous studies. However, as they considered this relation on a wider scope - that is, across H-R diagram, one interesting fact is that this relation gradually becomes dispersive as the temperature increases and nearly disappears in early-type stars.
"One intriguing question is what is the nature behind this trend, since the Rossby number is considered as the unique variable in stellar activity by previous studies," said Dr. YANG Huiqin. The study answers this question by proposing a scenario, in which the dynamo is the key point on revealing the relation among activity, structure and evolution.
"We present the overall picture of the activity - rotation relation. It has a dynamic variation across the H-R diagram, and this variation inspires us to reassess the classical activity-rotation relation," said LIU. They thereby suggested a new expression on the activity-rotation relation, which reflects the physical nature and is applicable for all types of stars.
This study, published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, was supported by the National Science Foundation of China. The paper includes data collected by the Kepler mission. Funding for the Kepler mission is provided by the NASA Science Mission Directorate.

Figure 1. Flare activity across H-R diagram. Black dots denote more than 200,000 Kepler stars. Colorful dots are the 3420 flaring stars. The color changes from blue to red, along with the increase of the flare activity. (Image by NAOC)
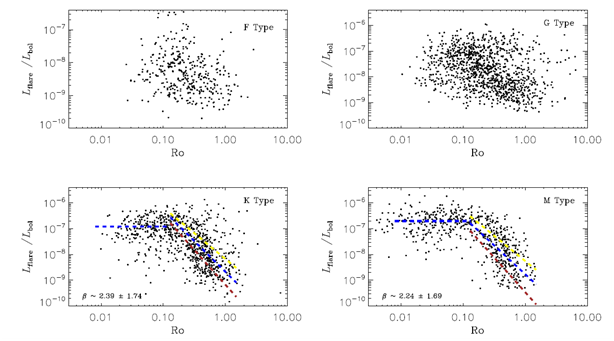
Figure 2. Activity - Rotation relation across H-R diagram. The relation is clear in late-type stars, whereas it gradually becomes dispersive as the temperature increases and nearly disappears in early-type stars. (Image by NAOC)
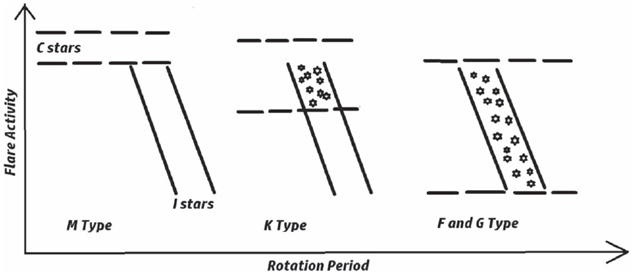
Figure 3. Sketch map of the activity - rotation relation on C and I stars. I stars always keep a power-law relation on the Rossby number, while C stars depend on the temperature. It illustrates the dynamic variation of the two types of star. (Image by NAOC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

