
Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Aiton) Hassk., also named as Rose myrtle, is distributed in hilly areas of Taiwan, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Lingnan region. R. tomentosa is a medicinal and ornamental plant, and its sweet fruit is edible. The leaves of R. tomentosa are used in the treatment of infectious diseases such as wound infections in Chinese traditional medicine.
Researchers from the South China Botanical Garden (SCBG), Chinese Academy of Sciences, studied the antibiotic-resistant bacteria activity and mechanism of the rhodomyrosone B, whose antibacterial active ingredient was from R. tomentosa.
They found rhodomyrosone B had strong antibacterial activity against Gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.62–1.25 μg/mL and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE) with an MIC of 2.5 μg/mL.
The membrane-targeting experiments revealed that rhodomyrosone B and its derivatives exhibited significant antibacterial activity with the perturbation of bacterial membrane potential and an increase in membrane permeability. They provided a detailed investigation of the antibacterial action of rhodomyrosone B against bacteria in vitro and in vivo.
By screening a series of synthetic derivatives for anti-resistant bacteria activity and structure-activity relationship (SAR), more active (up to 4-5 times) lead compounds were obtained and their antibacterial activity verified in vivo experiment.
Notably, rhodomyrosone B has profound antibacterial activity against drug-resistant bacteria (MRSA and VRE) as well as low cytotoxicity. It is bactericidal in nature, and an increase in membrane permeability resulting from membrane perturbation is one of its modes of action. Rhodomyrosone B represents a promising natural antibiotic to combat drug-resistant (MRSA and VRE) infections.
Related studies were published in Journal of Ethnopharmacology and Med. Chem. Commun.. The research results in rhodomyrosone B and plant-derived antibiotics provide a material basis for subsequent research on innovative anti-drug resistant antibiotics.
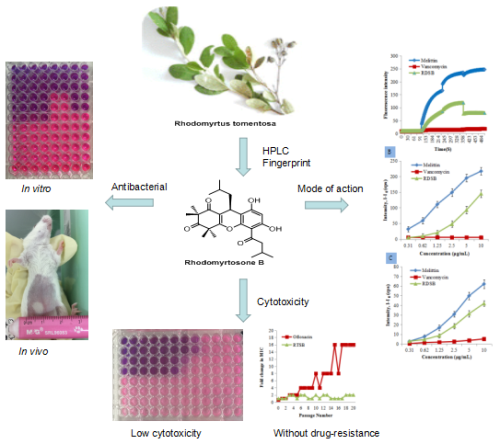
Fig.1 Rhodomyrtosone B, a membrane-targeting anti-MRSA natural acylgphloroglucinol from Rhodomyrtus tomentosa. (Image by SCBG)
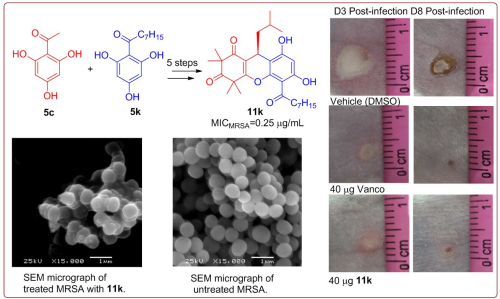
Fig.2 Structural optimization and antibacterial evaluation of rhodomytosone B analogues against MRSA strains. (Image by SCBG)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

