
Nowadays, environmental pollution has threatened human health and ecosystems in many aspects. In particular, aquatic ecosystems and human health have been seriously threatened by illegal discharge of wastewater.
To prevent such water pollution, rapid on-site pollutant detection program has to be established. However, currently, simple and effective monitoring methods are still sparse.
Recently, Assoc. Prof. ZHONG and Prof. ZHENG from the Institute of Urban Environment (IUE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has demonstrated a successful facile application of on-site aqueous pollutant monitoring using a flexible, ultralight and robust surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy substrate (SERS), which was formed by interfacial self-assembly of Au@Ag nanocubes (NCs) on a simultaneously formed polyvinyl chloride (PVC) template, followed by a thin coating of Au.
Compared to the traditional pollutant detection methods, their method has a much simpler sample preparation procedure, less detection time, and better detection efficiency.
Most importantly, it can in-situ detect surface contaminants on irregular objects. When combining with a portable Raman spectrometer, it can realize rapid on-site pollutants detection.
The novel substrate, Au@Ag@Au-NCs/PVC film, is flexible, ultralight, and robust and could float on the surface of water and firmly contact with water even under harsh environmental conditions. Moreover, the Au@ Ag@Au-NCs/PVC film is translucent, allowing penetration of laser beams and enhancement of Raman signals.
When thiram was used as a model contaminant in aqueous solution, a good linear relationship (R2 = 0.972) was obtained over the range of 0.1-50 ppb with a detection limit of 0.1 ppb.
Raman signals of thiram can be instantly and consecutively detected with the enhancement of the film in the simulated experiments, suggesting its possible use in the long run. Furthermore, the film can be easily regenerated by NaBH4 solution washing, which could reduce the operating cost.
Their work demonstrated a great potential in on-site pollutant monitoring in aqueous environments with a portable Raman spectrometer.
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and it was published in Environ. Sci. Technol.
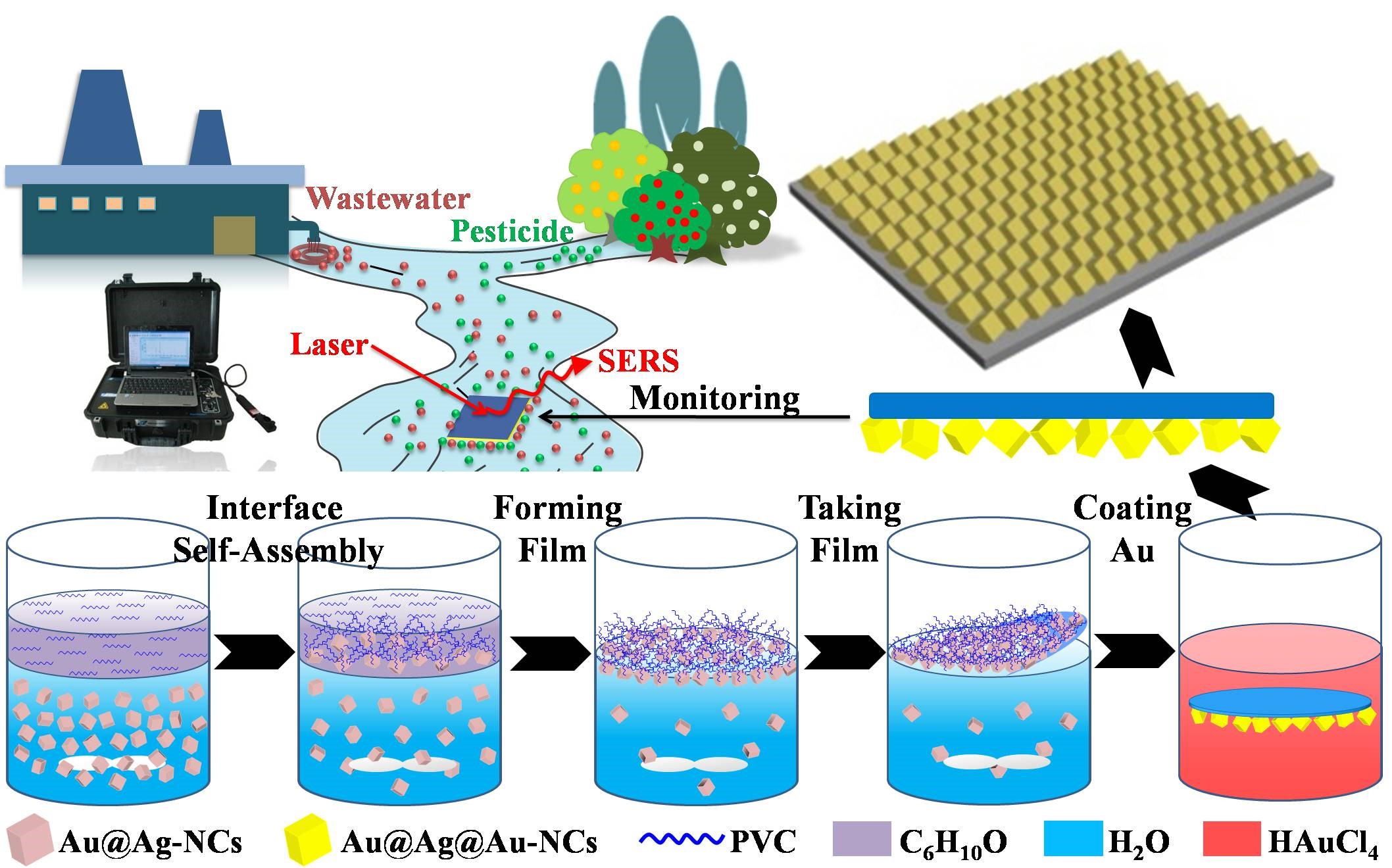
Schematic illustration of preparation of Au@Ag@Au-NCs/PVC film and its application as a SERS substrate for long-term on-site monitoring of contaminants in water bodies. (Image by ZHONG LuBin)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

