
The annual cycle is a key characteristic of the global monsoon system. It is crucial for drought/flood management in monsoon regions. However, the complexity of monsoon systems presents great challenges in simulating climatological seasonal means and annual cycles of the monsoons.
Increasing the horizontal resolution is considered a useful approach to improve monsoon simulation. Given the social and scientific importance of the onset and cessation of monsoonal precipitation to local livelihoods and economies, it is necessary to find out whether a higher resolution could systematically improve the representation of monsoon onset and withdrawal.
Under the Climate Science for Service Partnership: China (CSSP-China), scientists from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Reading, and the Met Office Hadley Centre compared the results of three Atmospheric General Circulation Models (AGCMs).
Their findings, recently published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, showed that increasing the resolution consistently could improve the simulation of precipitation and low-level circulation in terms of the annual mean and the first two annual cycle modes.
The researchers also found improvements in simulating the onset and withdrawal of summer monsoon, albeit with a degree of regional dependency. Higher resolution models showed consistent improvement in the simulation of early summer monsoon onset over East Asia and West Africa.
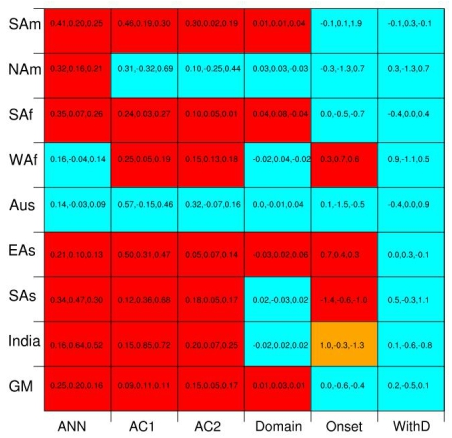
Improvement in the simulation of the annual cycle of global monsoon precipitation with horizontal resolution. Red boxes represent high resolution consistently improving the performance across all three AGCMs; blue boxes indicate improvement with resolution is inconsistent; orange boxes indicate a better simulation is shown in all three high-resolution AGCMs but the responses to resolution are inconsistent across models. (Image by ZHANG Lixia)
"It is important to carry out multi-model comparisons when examining the added value of resolution, and model physical parameterizations are still crucial for monsoon simulation," says ZHANG Lixia, first author of the study.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

