
PI3K/TSC/mTOR pathway plays a crucial role in multiple cellular behaviors, including cell survival, metabolism, proliferation, and autophagy and so on. Aberrant activation of this pathway is associated with protein translation, which is required for cell proliferation and survival in many types of cancers. The efforts of cancer genome sequencing have identified recurrent activating mutations of Rheb. It is a key molecular in PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in kidney and endometrial carcinoma. However, the role of this mutation in pathogenesis of these human cancers is still not well understood.
Disease Genomics Group from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP), led by Dr. LIU Yang, demonstrated a novel molecular mechanism of tumorigenesis in renal and endometrium carcinoma with activating mutation of Ras homolog enriched in brain (Rheb). The research provides a potential therapeutic strategy for Rheb-driven human cancers.
Dr. LIU's team showed that Rheb-Y35N mutation can not only lead to constitute “mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1” (mTORC1) activation, but sustained mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation. In addition, inhibition of both mTOR and MAPK pathway could significantly suppress Y35N-driven tumor growth in vitro and in vivo.
Furthermore, by collaborating with Dr. LI Guohui's research group, they found that Rheb can directly bind to the kinase domain of 5'AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPKα1) to regulate its activity. In contrast the Y35N mutant impairs AMPK activation by competitively binding to AMPKα, it can lead to attenuated pBRAF-S729. Consequently, the inhibitory site of BRAF activity subsequently sustained MEK-ERK activation.
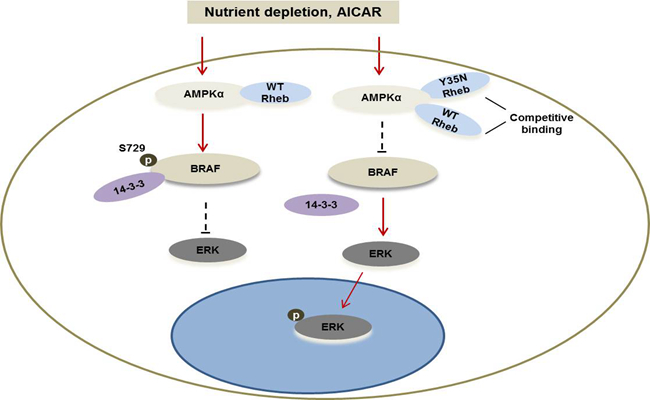
Proposed model for the interaction of Rheb with AMPK and regulation for MAPK pathway (Image by LIU Yang)
This study provided a novel insight into the cellular mechanism of Rheb-Y35N-driven tumor. It suggested a potential therapeutic approach and clinical basis to treat the tumor with Rheb-Y35N mutation. These results were published on Oncogene journal.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

