
Nonlinear optical (NLO) crystals, especially those generating middle and far infrared (IR) laser (3-20μm), have been attracted widespread attention because of their extensive applications in modern laser technology. An excellent IR NLO material should exhibit a large NLO coefficient (dij) and a wide optical bandgap (Eg). In view of the inverse relationship between the dij and Eg, how to balance the two parameters (dij > 10 × KDP and Eg > 3.0 eV) for IR NLO material has been a critical issue.
A research team led by Prof. PAN Shilie at the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry (XTIPC) of Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a new design strategy that incorporates the easily distorted MIVQ4 (MIV = Ge, Sn; Q = S, Se) ligands and large electropositive alkaline/alkaline-earth cations into crystal structures to discover the four new IR NLO materials, that is, Na2BaMQ4 (M=Ge, Sn; Q=S, Se).
In order to avoid the oxidation of raw materials in the high-temperature, researchers chose the vacuum-sealed silica tubes as the reaction devices. After the reaction, the product was carefully washed with N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) to remove the other byproducts. All of four crystals with different colors were stable in air for several months. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis showed that they crystallize in the different space groups, such as the I-42d for Na2BaSnS4 and R3c for other three materials.
These four materials show novel structural transformation from tetragonal to trigonal systems, whereas previous discovered structural changes in metal chalcogenides with the elements substitution (Sn to Ge, or S to Se) are mainly focused on following two forms: between the lower categories, and from the lower category to the intermediate category.
This structural transformation between the intermediate categories for title compounds can be considered as the first discovered examples in the known quaternary metal chalcogenides. Furthermore, this observation also indicates that the slight change of cation size may result in different structure features, and future structure prediction should be devoted considerable attentions to the different chalcogen atoms.
Researchers found Na2BaSnS4 and Na2BaGeS4 exhibit excellent properties with a suitable balance of Eg and dij measured for Na2BaSnS4 (3.27 eV and ~ 17 × KDP) and Na2BaGeS4 (3.70 eV and ~ 10 × KDP), demonstrating that the systems satisfy the key requirements as promising IR NLO candidates.
The result was published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
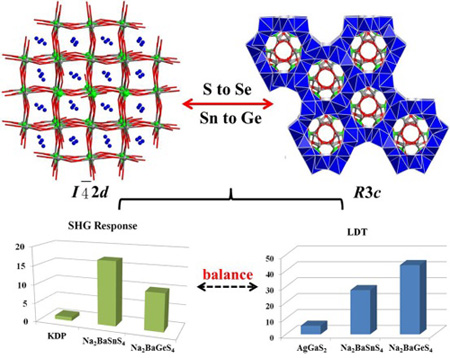
Figure: Structural changes and balanced properties of Na2BaMQ4 (M=Ge, Sn; Q=S, Se) (Image by XTIPC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

